ICD-10 Code R73.01
Impaired fasting glucose
What is the code R73.01?
The ICD-10-CM code R73.01 stands for "impaired fasting glucose." Code R73.01 is an International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code that healthcare providers and medical billers use to document and classify cases where patients exhibit abnormal fasting glucose levels that do not meet the criteria for a diabetes diagnosis.
Detailed description of R73.01
R73.01, impaired fasting glucose, is categorized under the ICD-10 chapter for symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified (R00–R99). This code is specifically used when a patient's fasting blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. The fasting glucose level typically ranges between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL. It’s an important marker for identifying patients at risk for diabetes, allowing for early intervention and management to prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms commonly associated with R73.01
Impaired fasting glucose (R73.01) itself is generally asymptomatic, meaning patients often do not exhibit noticeable symptoms. However, it is important to monitor for potential signs that may indicate a progression toward diabetes or other metabolic disorders. These signs can include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
In absence of a definitive diagnosis, code these symptoms in addition to R73.01.
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several ICD-10-CM codes are related to R73.01 and can be used for conditions that often present similarly or are part of the same diagnostic spectrum:
These codes help in distinguishing between different stages and types of glucose metabolism disorders.
Appropriate usage and guidelines for R73.01
All that needs to be documented to use code R73.01 are details such as "abnormal fasting glucose" and "elevated fasting glucose" by the clinician in the assessment and plan portion of the note.
Common pitfalls in coding with R73.01
Medical coders should be aware of several common pitfalls when using R73.01:
- Misclassification: Confusing R73.01 (impaired fasting glucose) with codes for diabetes (E11.x, E10.x) or other glucose abnormalities like R73.02 (impaired glucose tolerance) can lead to improper management plans and billing issues.
- Insufficient documentation: Claims may be denied if fasting glucose results are unclear or missing.
- Failure to update: If a patient develops diabetes or glucose levels normalize, update the code accordingly to avoid treatment and coverage issues.
Key resources for R73.01 coding
For accurate coding and documentation of R73.01, several resources can be invaluable:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting: Provides comprehensive guidelines for using ICD-10 codes.
- American Diabetes Association (ADA): Offers criteria and guidelines for diagnosing and managing prediabetes.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): Provides updates and information on coding and billing practices.
- Endocrinology textbooks and journals: Offer in-depth information on impaired fasting glucose and related conditions.
These resources can help ensure accurate and compliant coding practices.
Conclusion
Use ICD-10 code R73.01, impaired fasting glucose, to classify and document cases where patients exhibit abnormal fasting glucose levels. Accurate usage and documentation of this code are important for proper patient management and follow-up. By understanding the detailed description, symptoms, related codes, and guidelines, healthcare providers can effectively monitor and intervene in cases of impaired fasting glucose, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Using key resources and avoiding common pitfalls can further enhance the accuracy and efficacy of coding practices.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
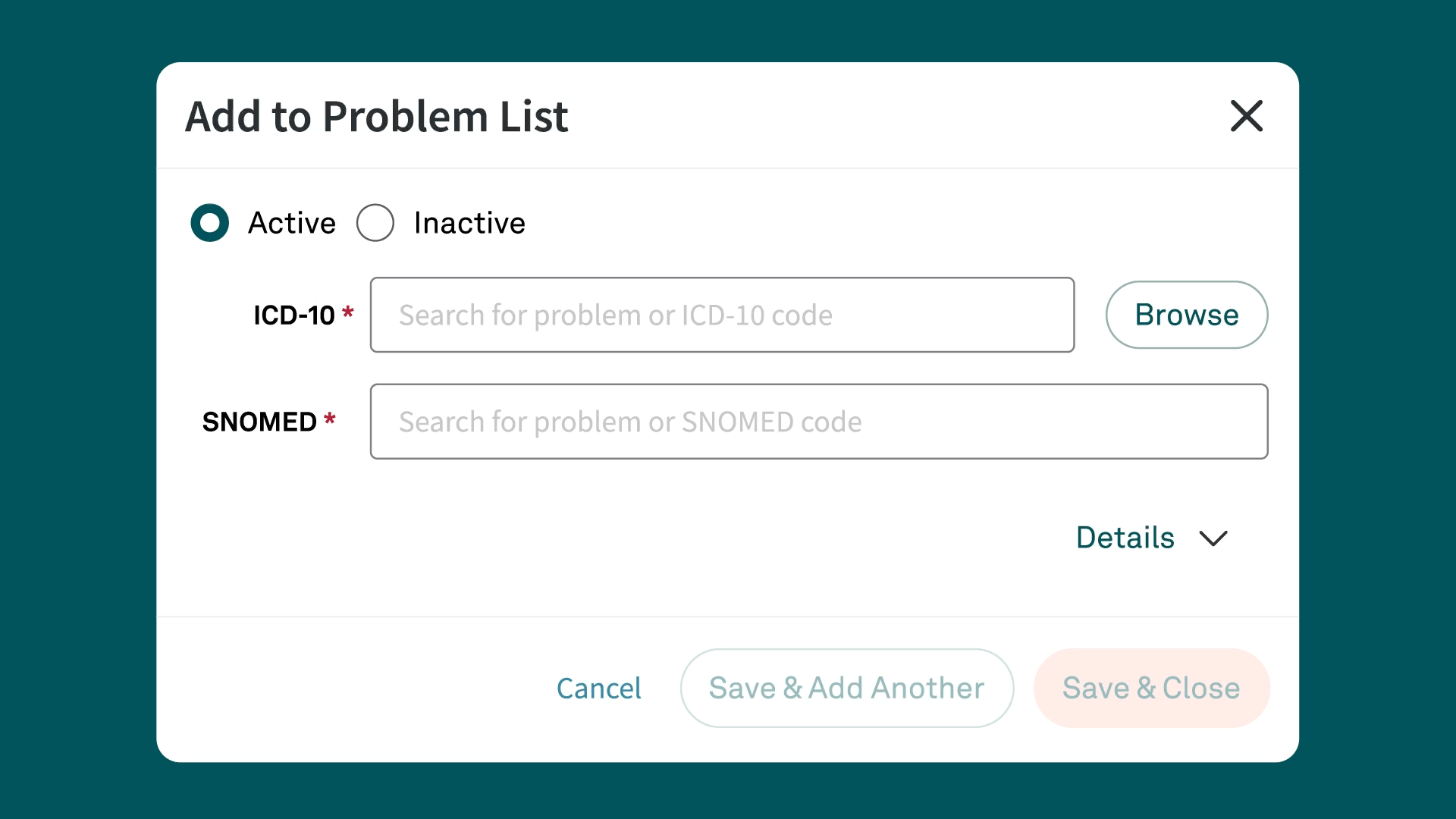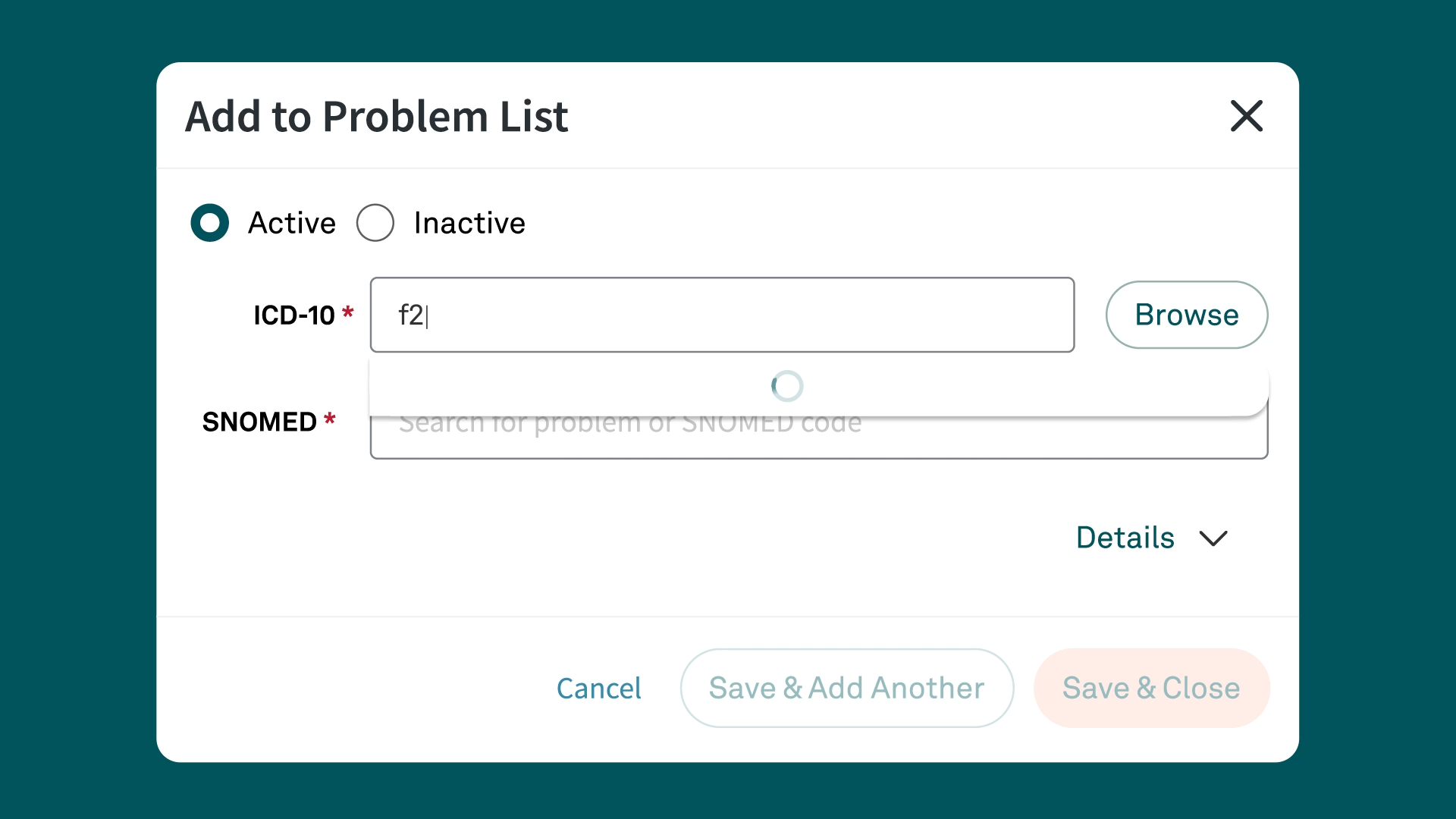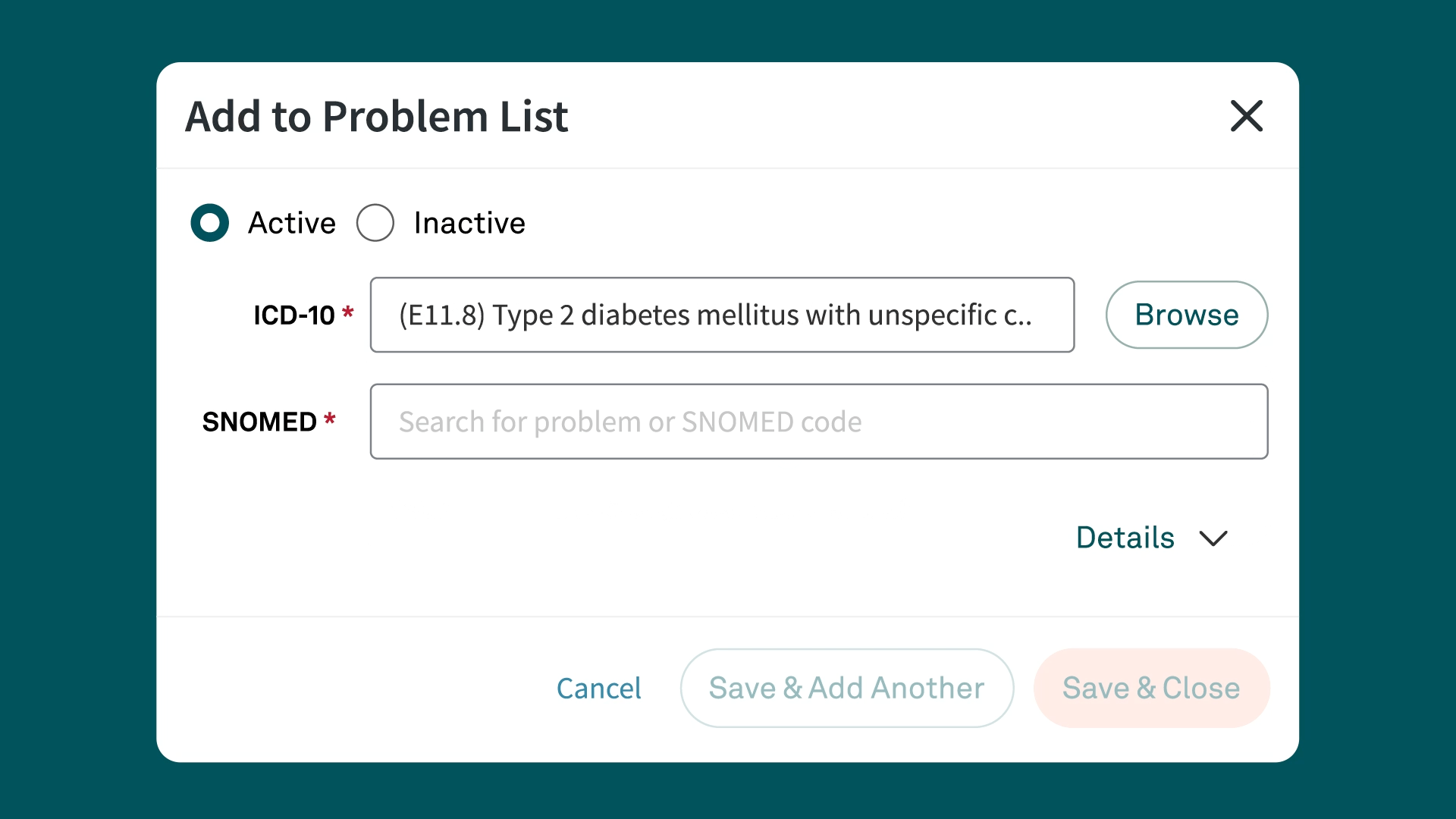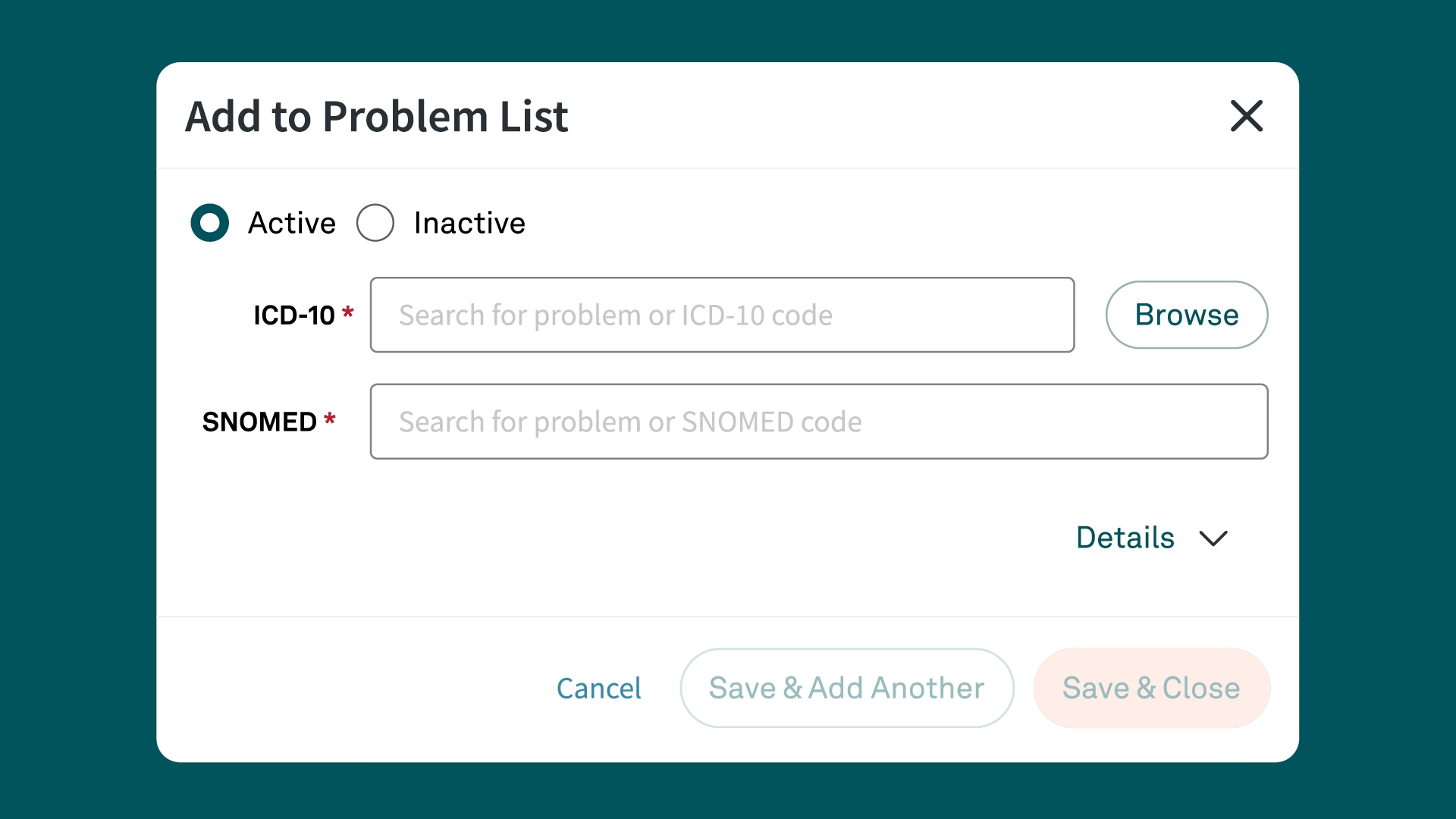
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Stay Ahead with Expert Healthcare & Billing Insights
Get the latest industry updates, financial tips, and expert strategies — delivered straight to your inbox.



