ICD-10 Code R31.9
Hematuria, unspecified
What is the code R31.9?
The ICD-10-CM code R31.9 is used to classify and document instances of hematuria, unspecified. Code R31.9 is an International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code that healthcare providers and medical billers use to document and classify diseases for medical documentation and billing. Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine, which can be visible to the naked eye (gross hematuria) or detectable only under a microscope (microscopic hematuria). The unspecified designation means that the exact cause or type of hematuria has not been determined.
Detailed description of R31.9
R31.9 falls under the ICD-10-CM chapter 18, which encompasses symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings not elsewhere classified. The code R31.9 is specifically used when a patient presents with blood in the urine, but the underlying cause hasn't been diagnosed. This could be due to a variety of conditions ranging from urinary tract infections (UTIs) to more serious conditions like kidney stones or malignancies. The unspecified nature of this code indicates that further diagnostic evaluation is needed to determine the exact cause of the hematuria.
Symptoms commonly associated with R31.9
Patients with hematuria (R31.9) may not always exhibit symptoms beyond the presence of blood in the urine. However, depending on the underlying cause, they might experience:
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Frequent urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Abdominal pain
- Flank pain
- Fever (if an infection is present)
- Nausea or vomiting (in cases of kidney stones)
Approximate synonyms for R31.9
The ICD-10 code R31.9 is used to classify cases of blood in the urine when the exact cause is unknown. Healthcare providers may use different terms to describe this condition, ensuring precise medical documentation and billing:
- Blood in urine
- Familial hematuria
- Hematuria (blood in urine)
- Hematuria, familial
- Hematuria, traumatic
- Traumatic hematuria
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several ICD-10 codes are related to hematuria and its specific types or causes:
- R31.0: Gross hematuria
- R31.1: Microscopic hematuria
- N30.00: Acute cystitis without hematuria
- N20.0: Calculus of kidney
- C67.9: Malignant neoplasm of bladder, unspecified
These related codes help in specifying the type or cause of hematuria, aiding in more precise diagnosis and treatment.
Appropriate usage and guidelines for R31.9
Use the code R31.9 when a patient presents with hematuria, and the specific type or cause has not been identified. It's appropriate to use this code in the initial stages of diagnosis when further tests are needed to pinpoint the source of the blood in the urine. Medical providers should ensure comprehensive documentation, including patient history, physical examination findings, and initial test results, to support the use of this unspecified code. Once a more specific diagnosis is made, the code should be updated accordingly.
Common pitfalls in coding with R31.9
One common pitfall in using R31.9 is failing to update the code once a specific diagnosis is made. For instance, if further testing reveals that the hematuria is due to a urinary tract infection or kidney stones, the code should be revised to reflect the more precise diagnosis. Another pitfall is overuse of the unspecified code without adequate diagnostic follow-up, which can lead to incomplete patient records and potential issues with insurance reimbursement.
Key resources for R31.9 coding
Several key resources can assist medical coders and healthcare providers in accurately using the R31.9 code:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting
- American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines on hematuria
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) information on hematuria
- Clinical documentation improvement programs and resources
- Coding manuals and software provided by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
These resources provide detailed information on coding guidelines, clinical best practices, and updates on coding standards.
Conclusion
Use ICD-10 code R31.9 to document instances of unspecified hematuria. Properly applying this code requires comprehensive initial patient evaluation and thorough documentation. While it serves as an initial diagnostic code, it is important to update it once a more specific diagnosis is established. By adhering to coding guidelines and using available resources, healthcare providers can ensure accurate and effective patient care and documentation.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
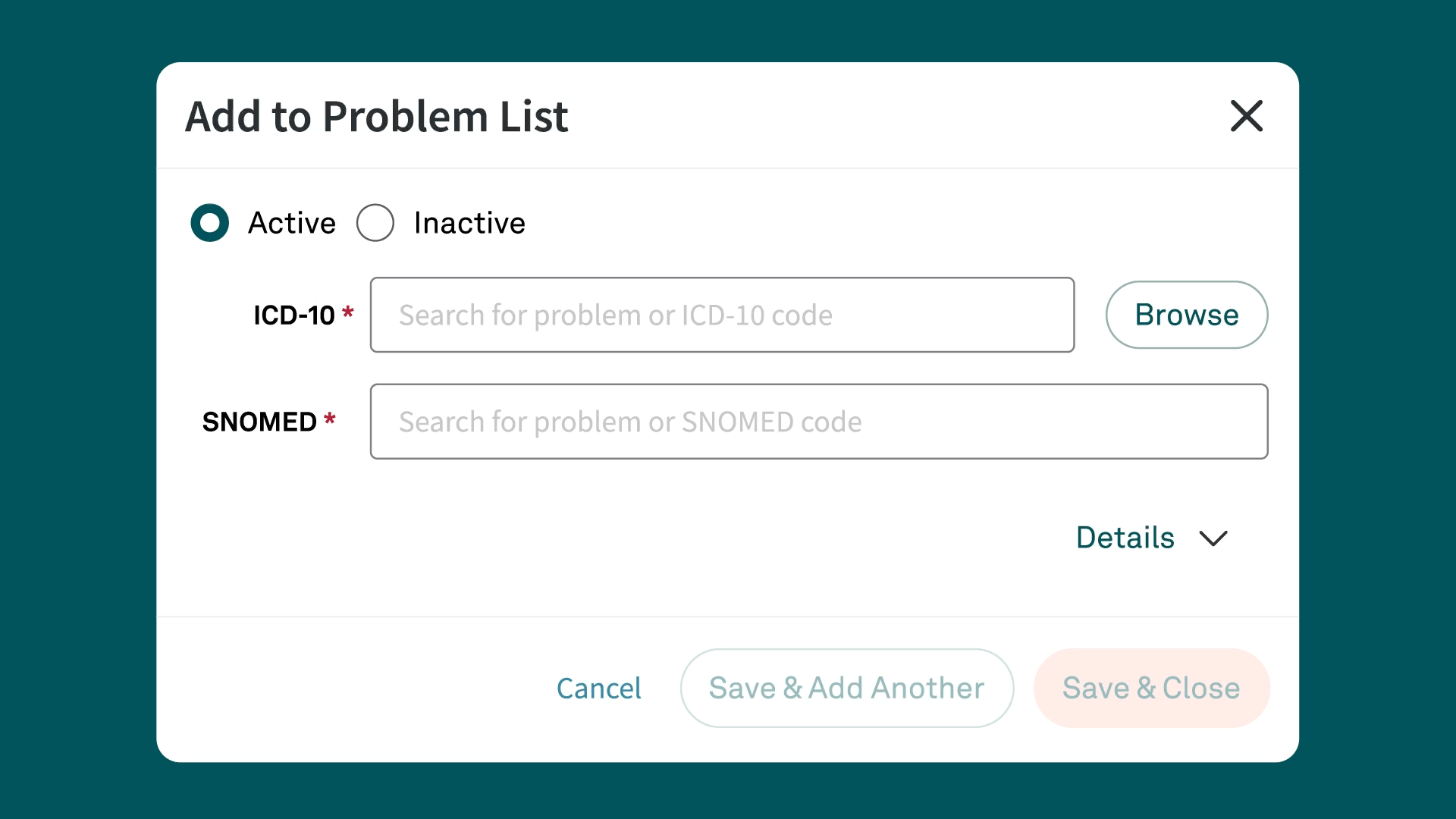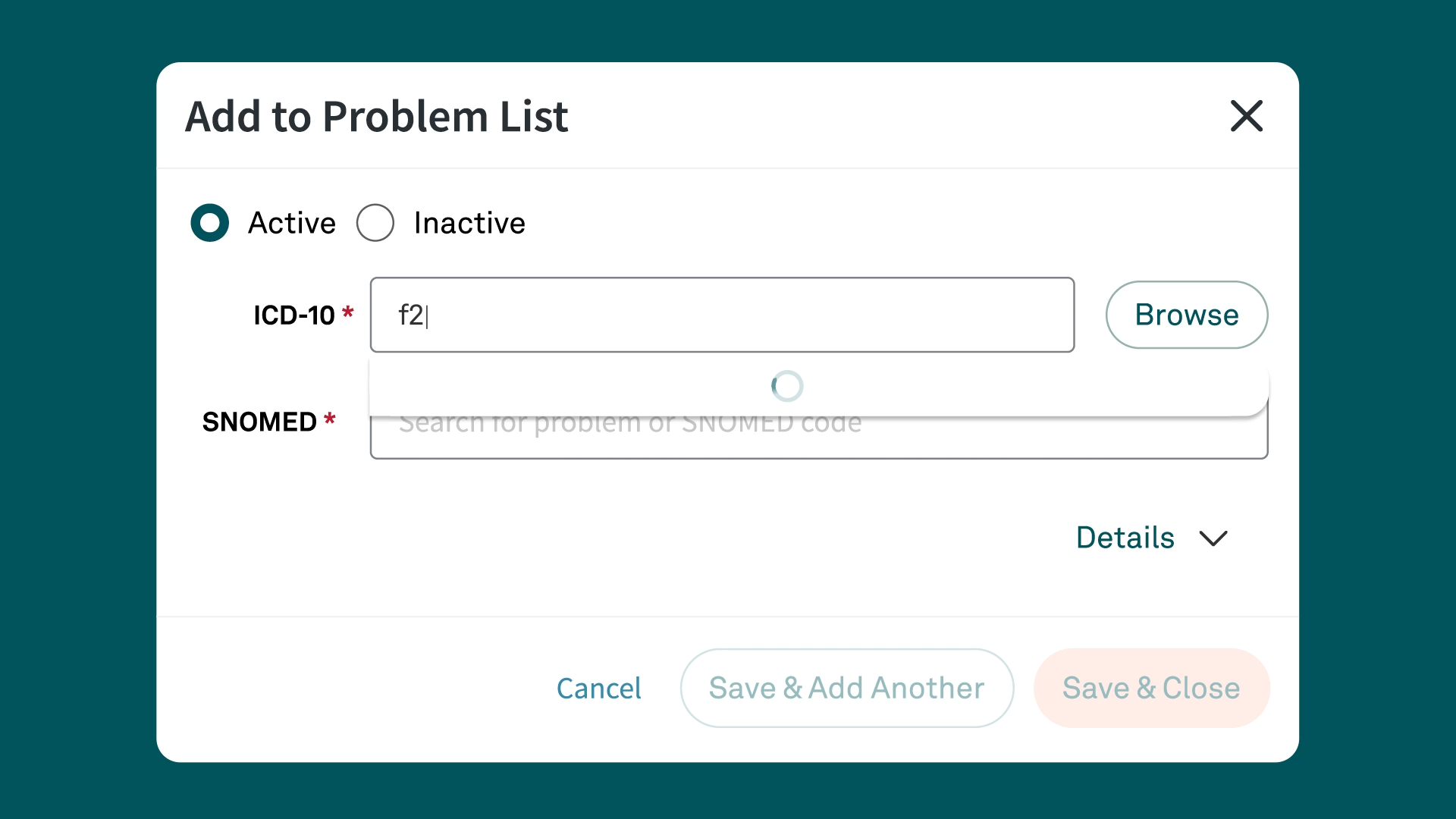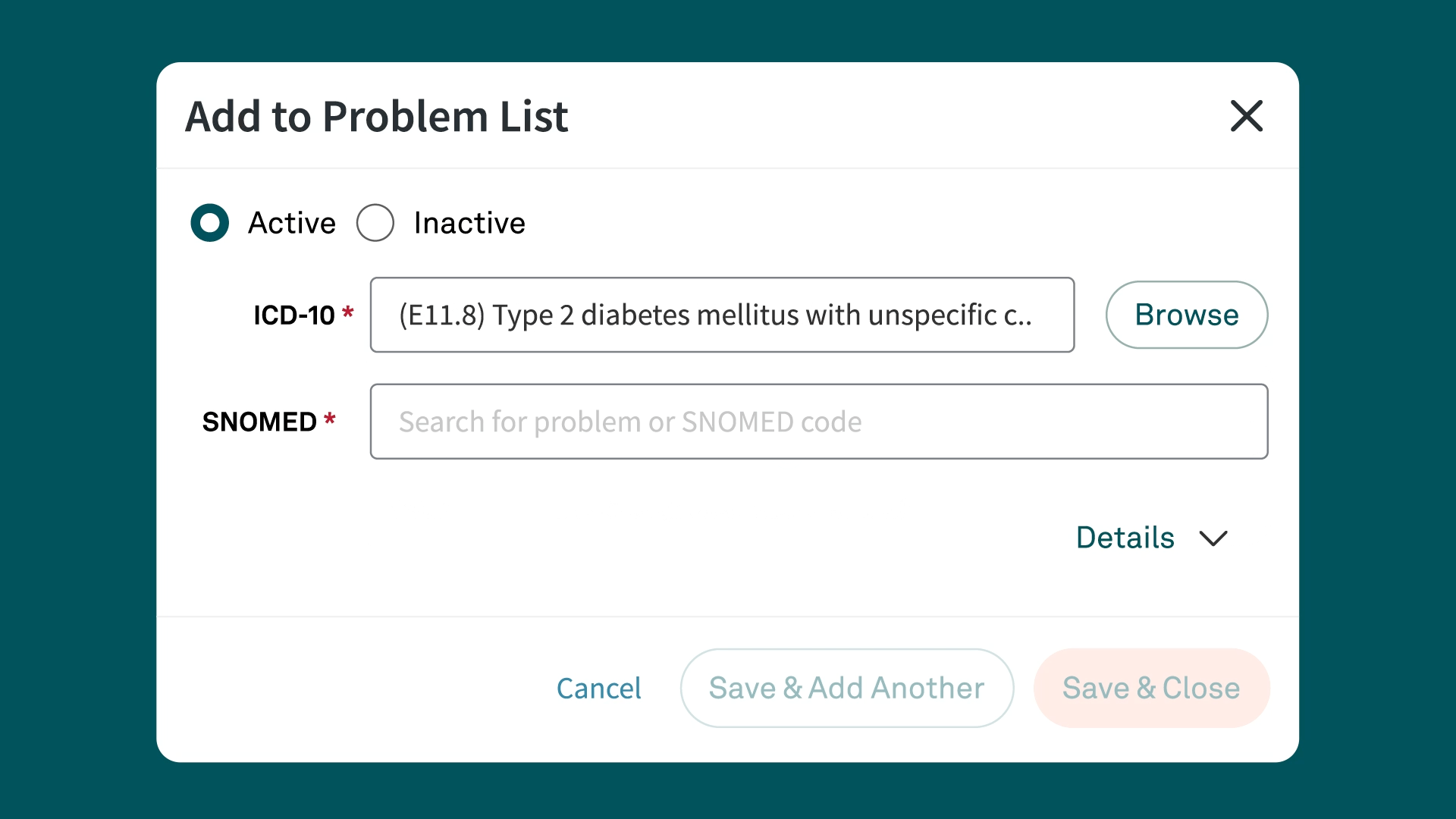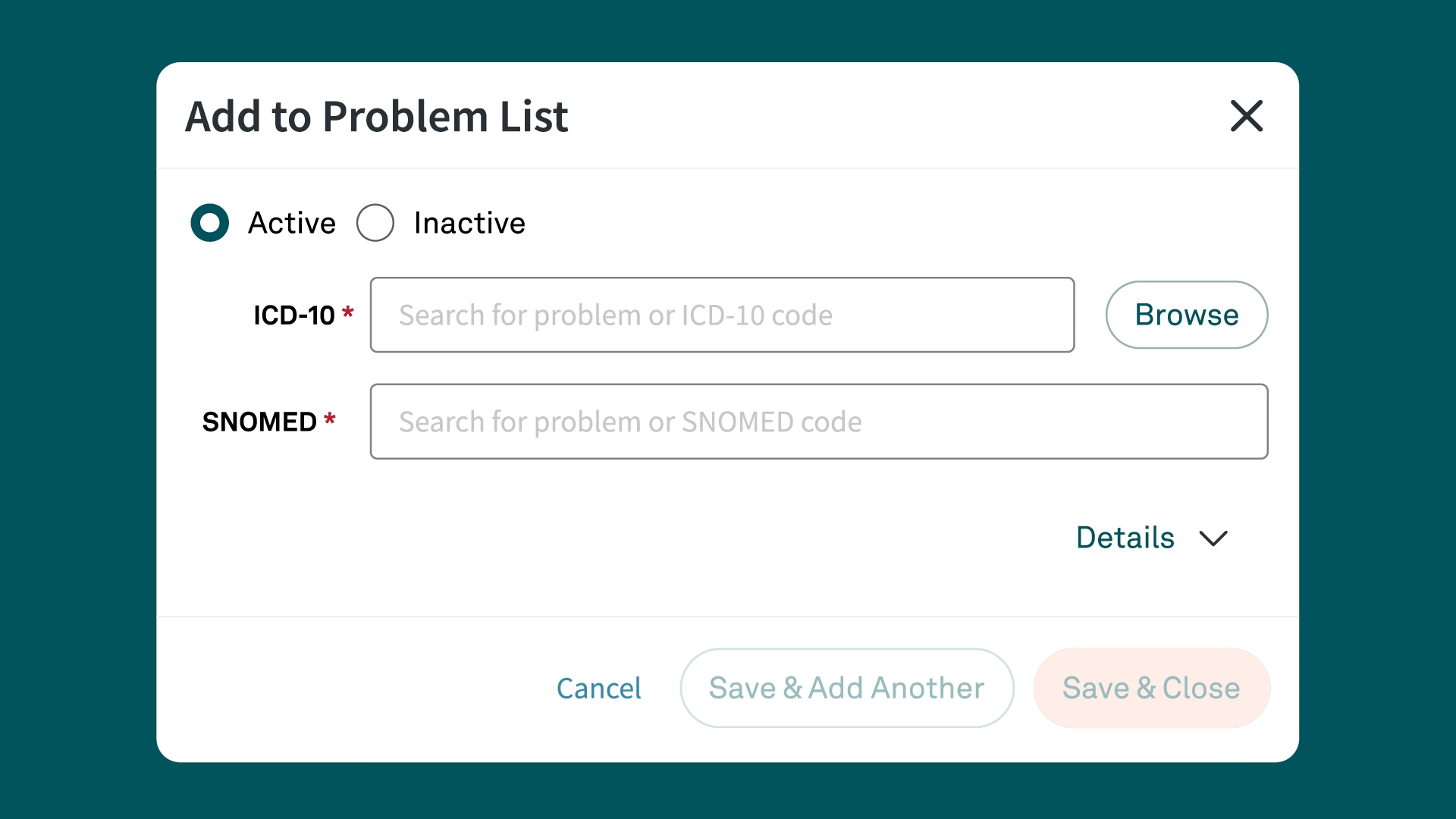
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Stay Ahead with Expert Healthcare & Billing Insights
Get the latest industry updates, financial tips, and expert strategies — delivered straight to your inbox.



