ICD-10 Code R30.0
Dysuria — pain or discomfort during urination
What is the code R30.0?
R30.0 is an ICD-10-CM code used to specify a diagnosis of dysuria. Dysuria is characterized by pain or discomfort during urination. This code is used by healthcare providers to document and communicate this specific symptom for billing and medical record purposes.
Detailed description of R30.0
R30.0 denotes dysuria which is painful or difficult urination. It is often a symptom of urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder infections, or other underlying urological issues. Dysuria can affect both men and women and may be accompanied by other urinary symptoms such as frequency, urgency, or hematuria.
Symptoms commonly associated with R30.0
Patients diagnosed with R30.0 typically experience pain, burning, or discomfort during urination. Other associated symptoms can include:
- Increased frequency of urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Lower abdominal pain
- Hematuria (blood in urine)
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several ICD-10 codes are related to or similar to R30.0. These include:
- N39.0: Urinary tract infection, site not specified
- N30.00: Acute cystitis without hematuria
- N30.01: Acute cystitis with hematuria
- N34.1: Nonspecific urethritis
- R35.0: Frequency of micturition
- R39.15: Urgency of urination
Appropriate usage of R30.0 for billing
Use R30.0 when a patient presents with dysuria, and the provider has documented this diagnosis in the medical record. It is important to ensure that the symptom is clearly noted in the patient's assessment to support the use of this code. Do not assign R30.0 if a more specific underlying condition is identified and documented.If the underlying etiology of the dysuria has been diagnosed by the provider, that condition should be coded instead of R30.0.
Instructional guidelines for coding R30.0
- “Strangury“ is an inclusion term for R30.0 and is an alternative term for which R30.0 may be used.
- According to the ICD-10-CM Guidelines Section IV.D., Diagnostic Coding and Reporting Guidelines for Outpatient Services, codes that describe symptoms and signs, as opposed to diagnoses, are acceptable for reporting purposes when a diagnosis has not been established (confirmed) by the provider. Chapter 18 of ICD-10-CM, Symptoms, Signs, and Abnormal Clinical and Laboratory Findings Not Elsewhere Classified (codes R00–R99) contain many, but not all codes for symptoms.
- Refer to the ICD-10-CM guidelines section I.B.4., section I.C.18.a, and section I.C.18.b regarding proper coding of signs and symptoms, use of symptom codes and use of symptom codes with a definitive diagnosis code for general guidance that is applicable to coding R30.0.
Common pitfalls in coding with R30.0
- Coding R30.0 when dysuria is not explicitly documented in the medical record.
- Using R30.0 when a more specific condition is present.
- Misinterpreting similar symptoms or conditions and incorrectly using R30.0.
Key resources for R30.0 coding
For accurate coding of R30.0, the following resources can be helpful:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting
- American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA)
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) ICD-10 resources
- Professional coding manuals and software tools
- Continuing education and coding certification programs
Conclusion
R30.0 is the ICD-10-CM code for dysuria, which is painful or difficult urination. Accurate coding of R30.0 requires clear documentation of the symptom and an understanding of related symptoms and conditions. By adhering to coding guidelines and avoiding common pitfalls, healthcare providers can ensure proper billing and effective communication of patient diagnoses.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
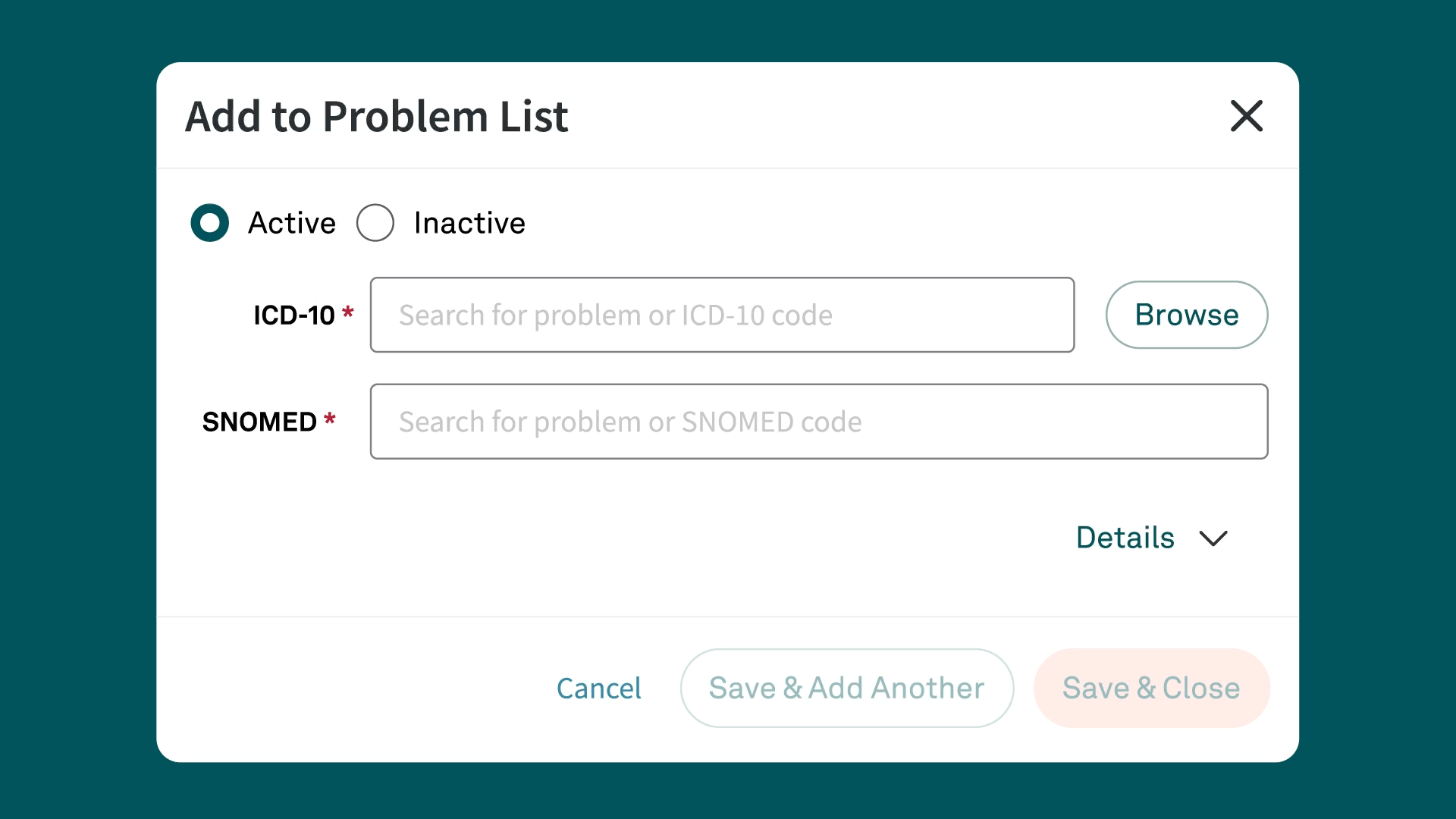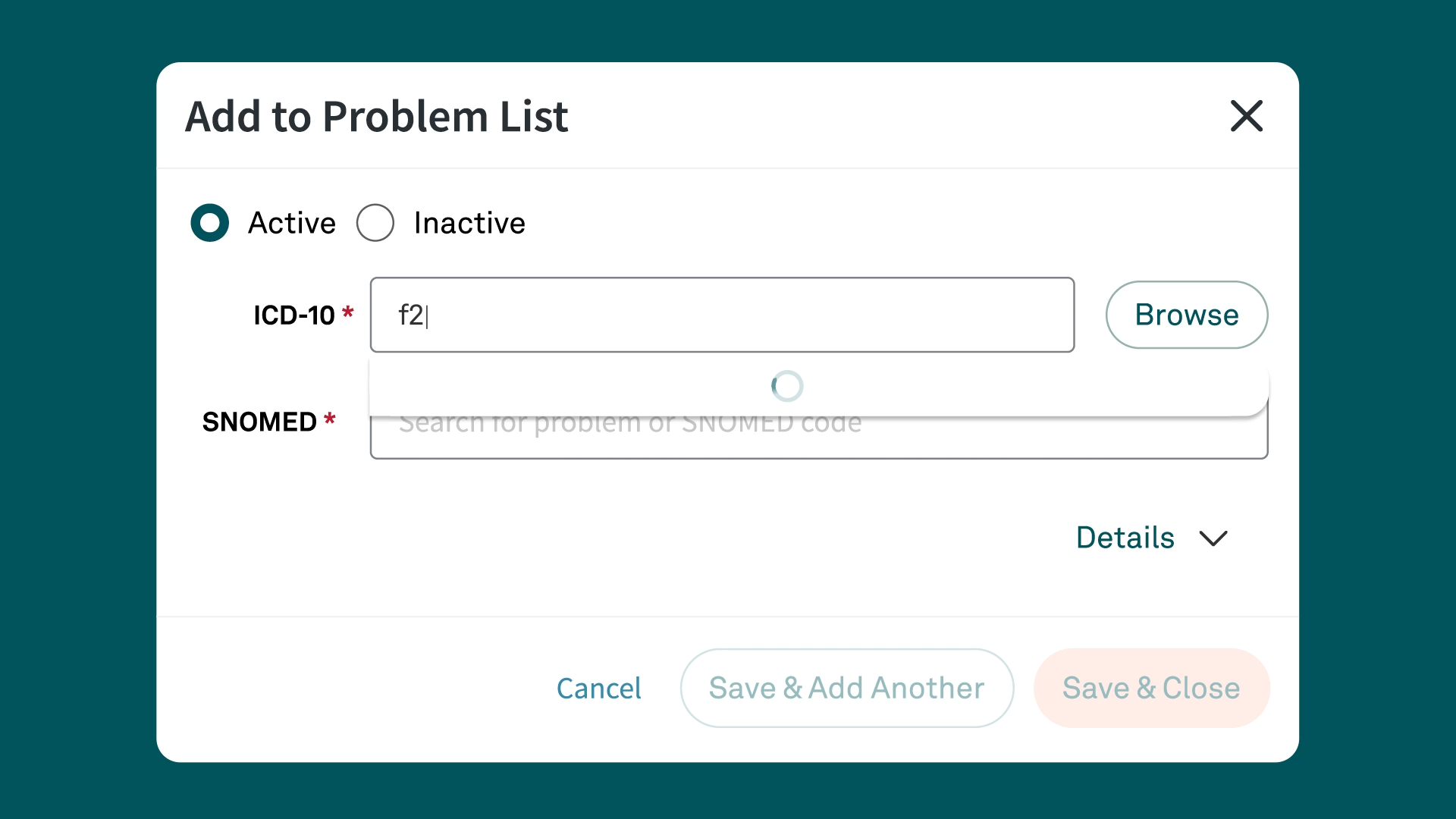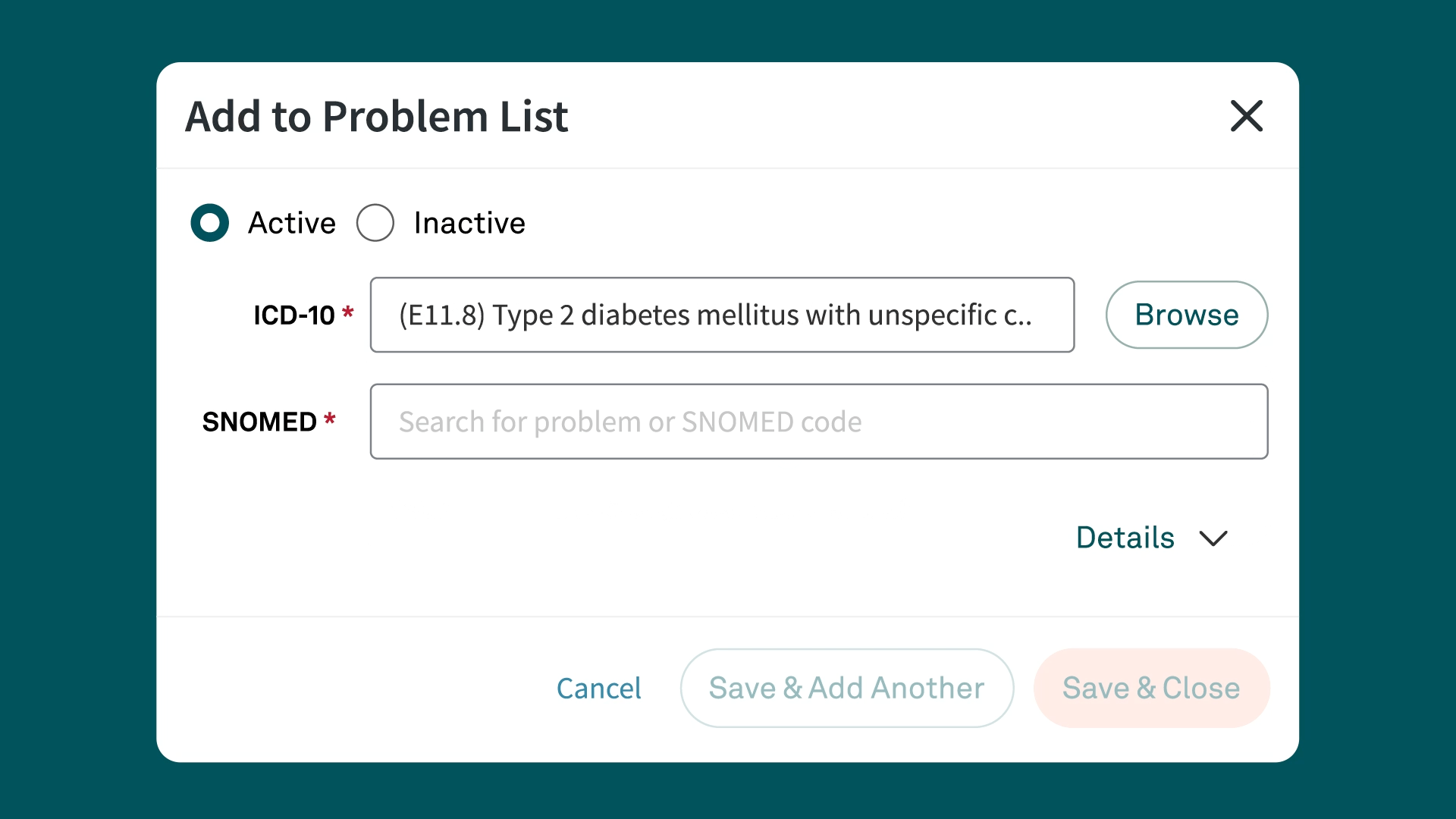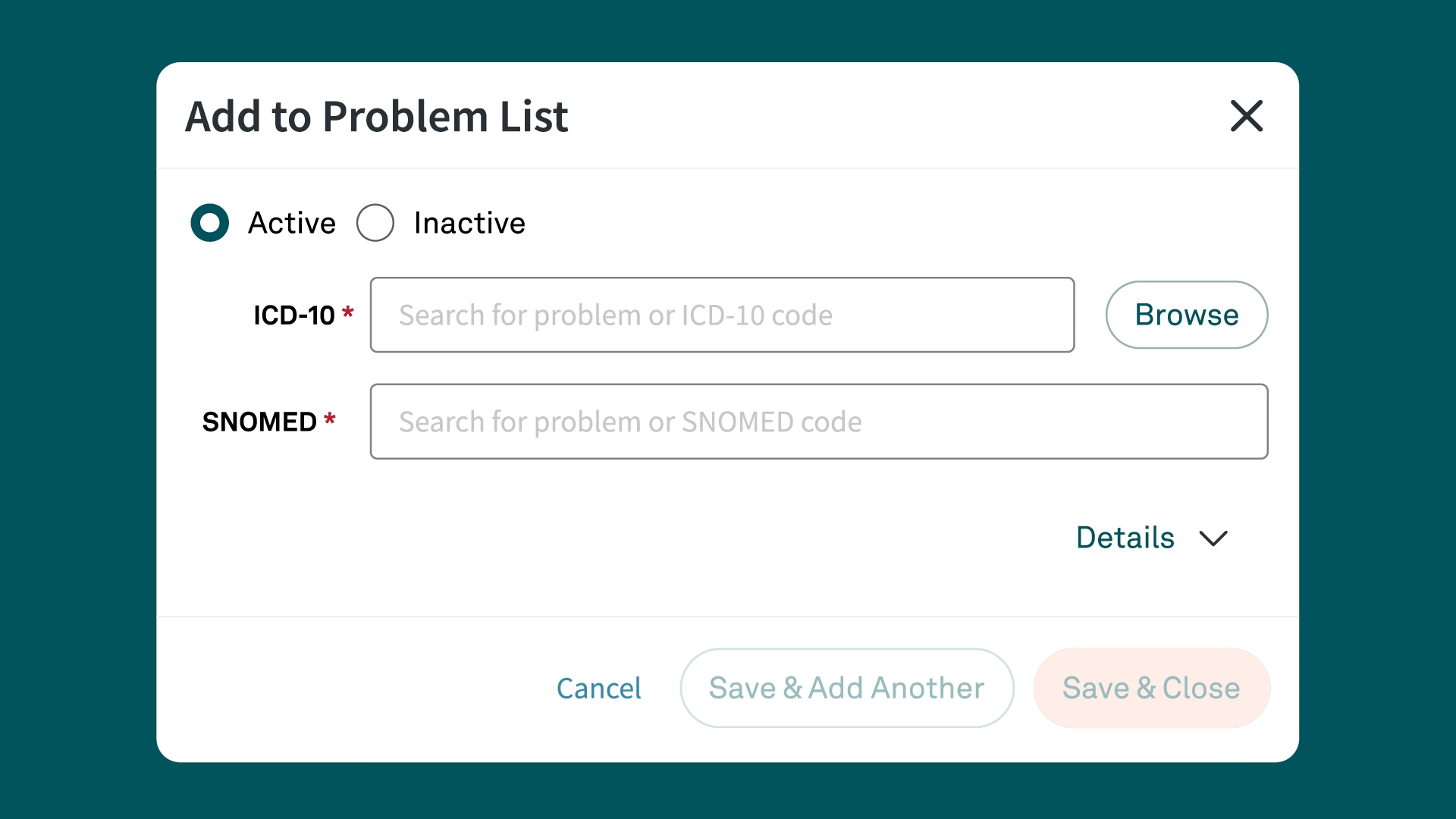
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Subscribe to The Intake:
A weekly check-up for your independent practice



