ICD-10 Code R06.02
Shortness of breath
R06.02 is an ICD-10-CM code used to classify and document instances of shortness of breath. This code is part of the ICD-10 chapter 18, which covers symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings that are not classified elsewhere.
Detailed description of R06.02
Shortness of breath is a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity. It is a common symptom in various respiratory and cardiovascular conditions, and it can also be associated with anxiety and other psychological factors.
Symptoms commonly associated with R06.02
Symptoms commonly associated with shortness of breath (R06.02) include:
- Difficulty breathing
- A feeling of tightness in the chest
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Fatigue or exhaustion after minimal exertion
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
- R06.00: Dyspnea, unspecified
- R06.01: Orthopnea
- R06.03: Acute respiratory distress
- R06.09: Other forms of dyspnea
- J45.909: Unspecified asthma, uncomplicated
Appropriate usage of R06.02 for billing
R06.02 should be used for billing when a patient presents with shortness of breath that requires medical evaluation and management that has not been attributed to a definitive underlying condition. It is important to document the clinical context and any associated conditions or symptoms to justify the use of this code. This ensures appropriate reimbursement and accurate medical records.
Instructional guidelines for coding R06.02
When coding for R06.02, ensure that the diagnosis is supported by the patient's medical history, clinical examination, and any relevant diagnostic tests. Always confirm that shortness of breath is the primary symptom being addressed, and not a secondary symptom related to a more specific condition that should be coded instead of R06.02.
Refer to the ICD-10-CM guidelines for chapter 18 (Symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified) to ensure proper use of R06.02. Be aware of the need to code more specific diagnoses instead of R06.02 if they are present and documented.
There is an excludes 1 note found at category R06, abnormalities of breathing that is applicable to code R06.02 for the following conditions:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (J80)
- Respiratory arrest (R09.2)
- Respiratory arrest of newborn (P28.81)
- Respiratory distress syndrome of newborn (P22.–)
- Respiratory failure (J96.–)
- Respiratory failure of newborn (P28.5)
Due to this instructional note, when the patient has been diagnosed with one of the listed conditions, only the condition noted in the excludes 1 note should be assigned and R06.02 would be omitted.
Common pitfalls in coding with R06.02
- Using R06.02 as a catch-all for any respiratory distress without thorough documentation.
- Failing to distinguish between different types of dyspnea, such as orthopnea (R06.01) or acute respiratory distress (R06.03).
- Overlooking underlying conditions that may have their own specific codes, leading to incomplete or inaccurate coding.
Key resources for R06.02 coding
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting
- American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) resources
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) coding resources
- Clinical documentation improvement (CDI) programs and materials
Conclusion
R06.02 is an ICD-10-CM code for documenting shortness of breath. Proper use of this code involves detailed clinical documentation, awareness of related codes, and adherence to coding guidelines. By following best practices, healthcare providers can ensure accurate billing and effective patient care management.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
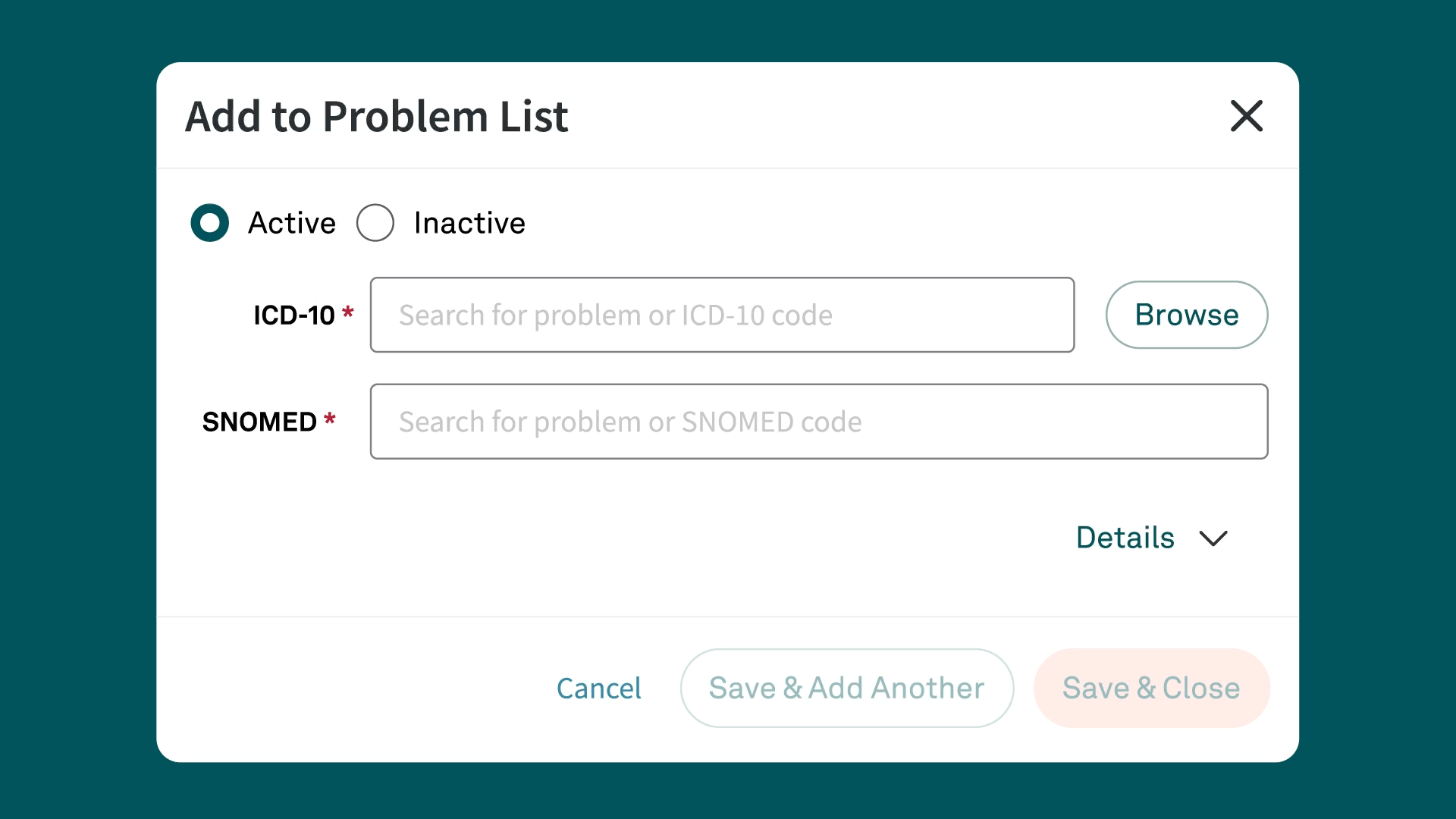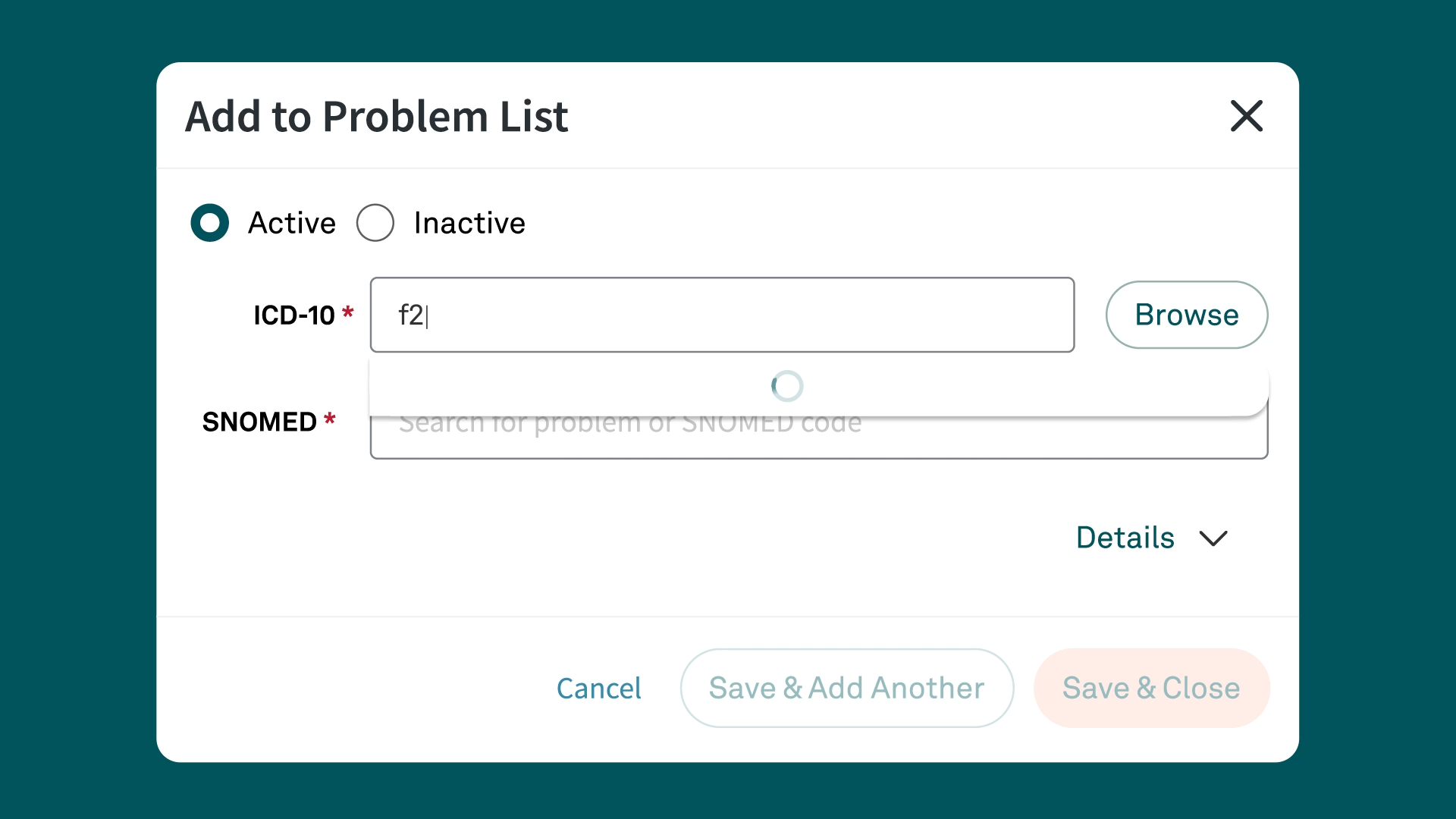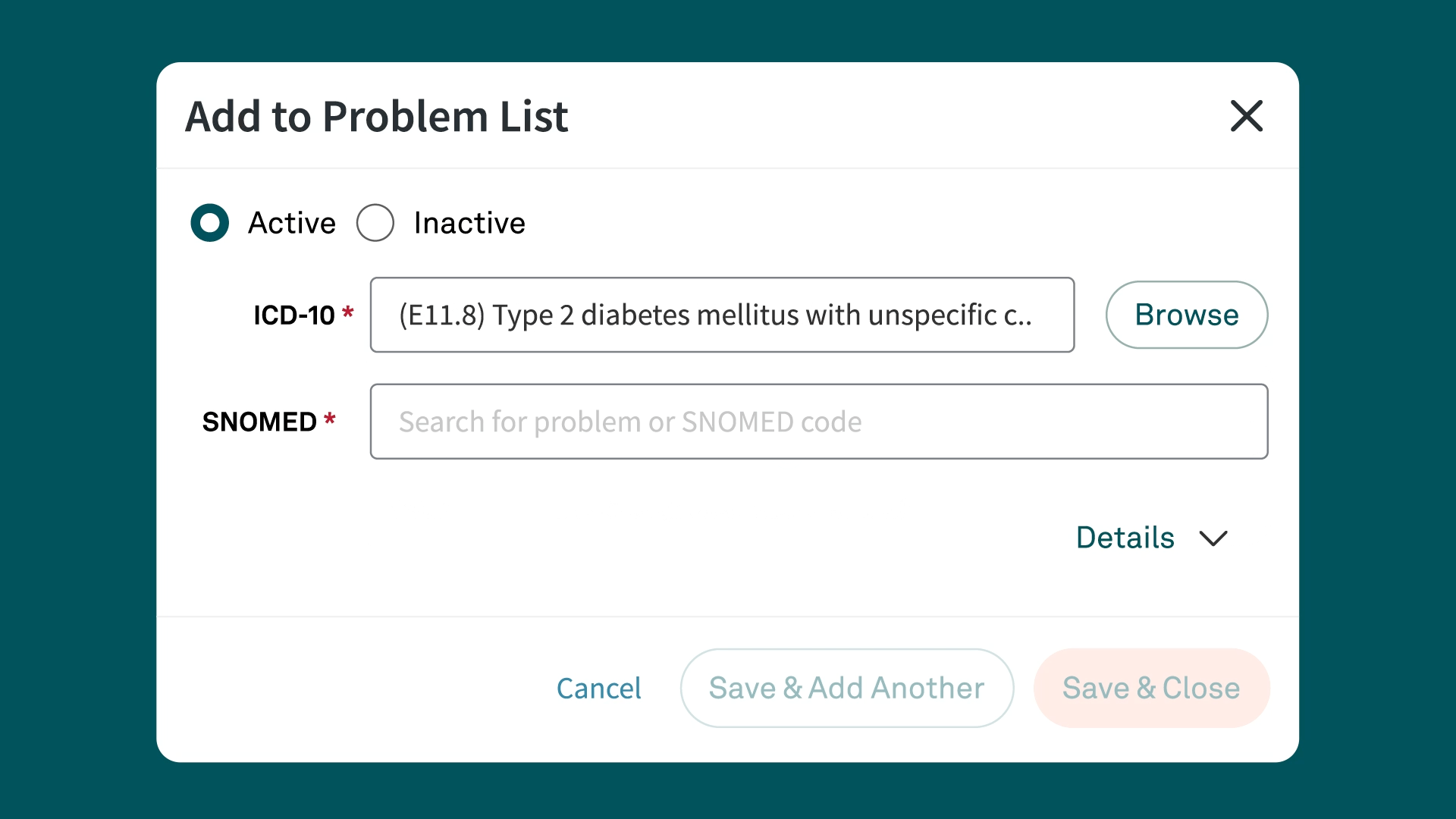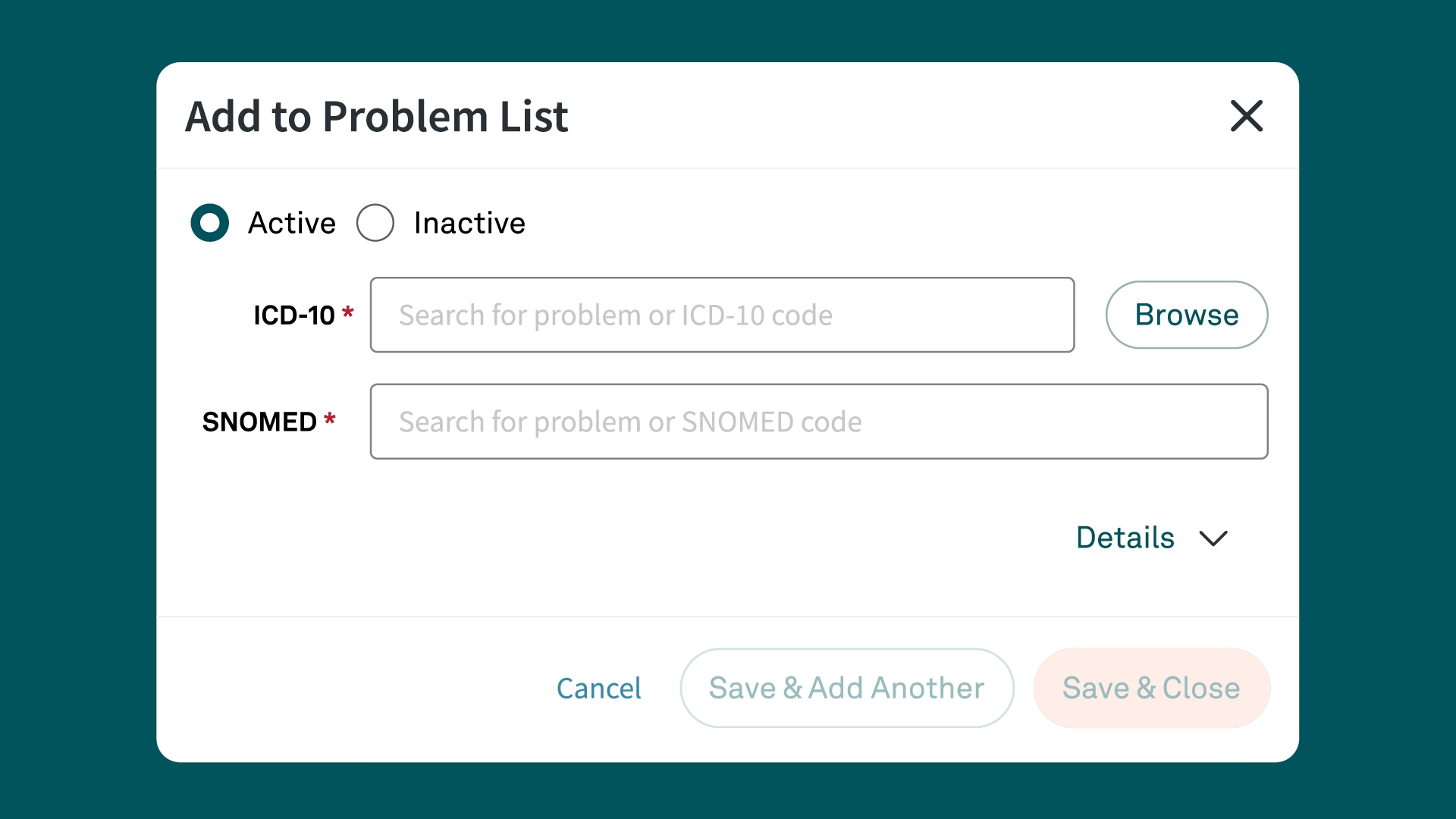
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Subscribe to The Intake:
A weekly check-up for your independent practice



