ICD-10 Code K70.30
Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver without ascites
What is the code K70.30?
The ICD-10-CM code K70.30 represents “alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver without ascites.” This code falls under the category of diseases of the digestive system, specifically those related to the liver. The classification is used by physicians and medical coders to document and categorize medical diagnoses for billing and treatment purposes.
Detailed description of K70.30
Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver without ascites (K70.30) refers to cirrhosis of the liver caused by prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption. Cirrhosis is characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, which impairs the liver's functionality. K70.30 specifically indicates that there is no presence of ascites, which is the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. This condition is serious and can lead to a range of complications, including liver failure.
Symptoms commonly associated with K70.30
Patients diagnosed with alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver without ascites may exhibit various symptoms, including:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Itchy skin
- Spider angiomas (small, spider-like blood vessels visible under the skin)
- Redness on the palms of the hands
- Confusion or difficulty thinking clearly (hepatic encephalopathy)
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several ICD-10 codes are related to K70.30, each representing different aspects or complications of liver disease:
- K70.31: Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver with ascites
- K70.2: Alcoholic fibrosis and sclerosis of the liver
- K74.60: Unspecified cirrhosis of liver
- K74.69: Other cirrhosis of liver
- K76.0: Fatty (change of) liver, not elsewhere classified
Appropriate usage and guidelines for K70.30
When documenting and coding for alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver without ascites (K70.30), ensure that the diagnosis is well-documented in the patient's medical record. The provider documentation should clearly link the cirrhosis as due to alcohol. If the provider has documented the presence of ascites, K70.30 should not be used.
Common pitfalls in coding with K70.30
Common pitfalls in coding K70.30 include:
- Failing to distinguish between cirrhosis with and without ascites, which can lead to incorrect coding.
- Failure to document the underlying cause of cirrhosis as alcohol-related may result in a less specific code being assigned. It is necessary to identify the cause of cirrhosis in order to ensure proper coding.
- Using K70.30 when another code might more accurately represent the patient's condition, such as K70.31 if ascites is present.
Key resources for K70.30 coding
For accurate coding of K70.30, the following resources can be invaluable:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting: These guidelines provide comprehensive instructions for using ICD-10 codes.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS offers a wealth of resources and updates on coding practices, including webinars, manuals, and bulletins.
- Professional coding organizations: Organizations like the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) offer educational resources, certifications, and support for medical coders.
- Coding reference books and software: Reference materials such as the ICD-10-CM codebook can support medical coders and providers.
These resources provide detailed instructions and updates on coding standards and practices.
Conclusion
Use ICD-10-CM code K70.30 to document alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver without ascites, a serious condition resulting from chronic alcohol abuse. Accurate coding requires thorough documentation of the patient's condition, including identifying the underlying cause of the cirrhosis as due to alcohol as well as the presence or absence of ascites. A clear understanding of related codes and potential pitfalls is important for accurate coding. Leveraging key resources and adhering to coding guidelines ensures precise and effective medical billing and treatment planning.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
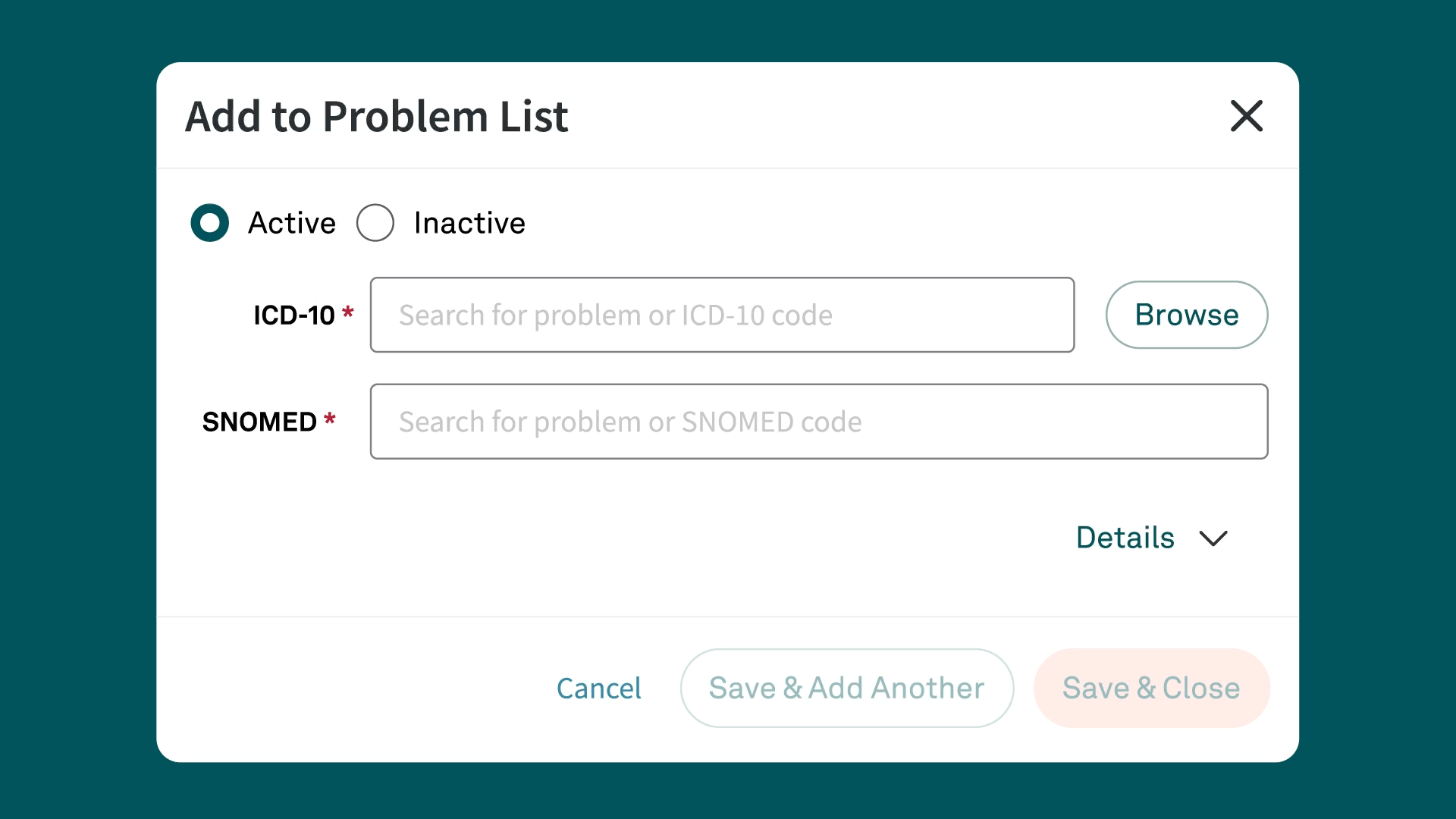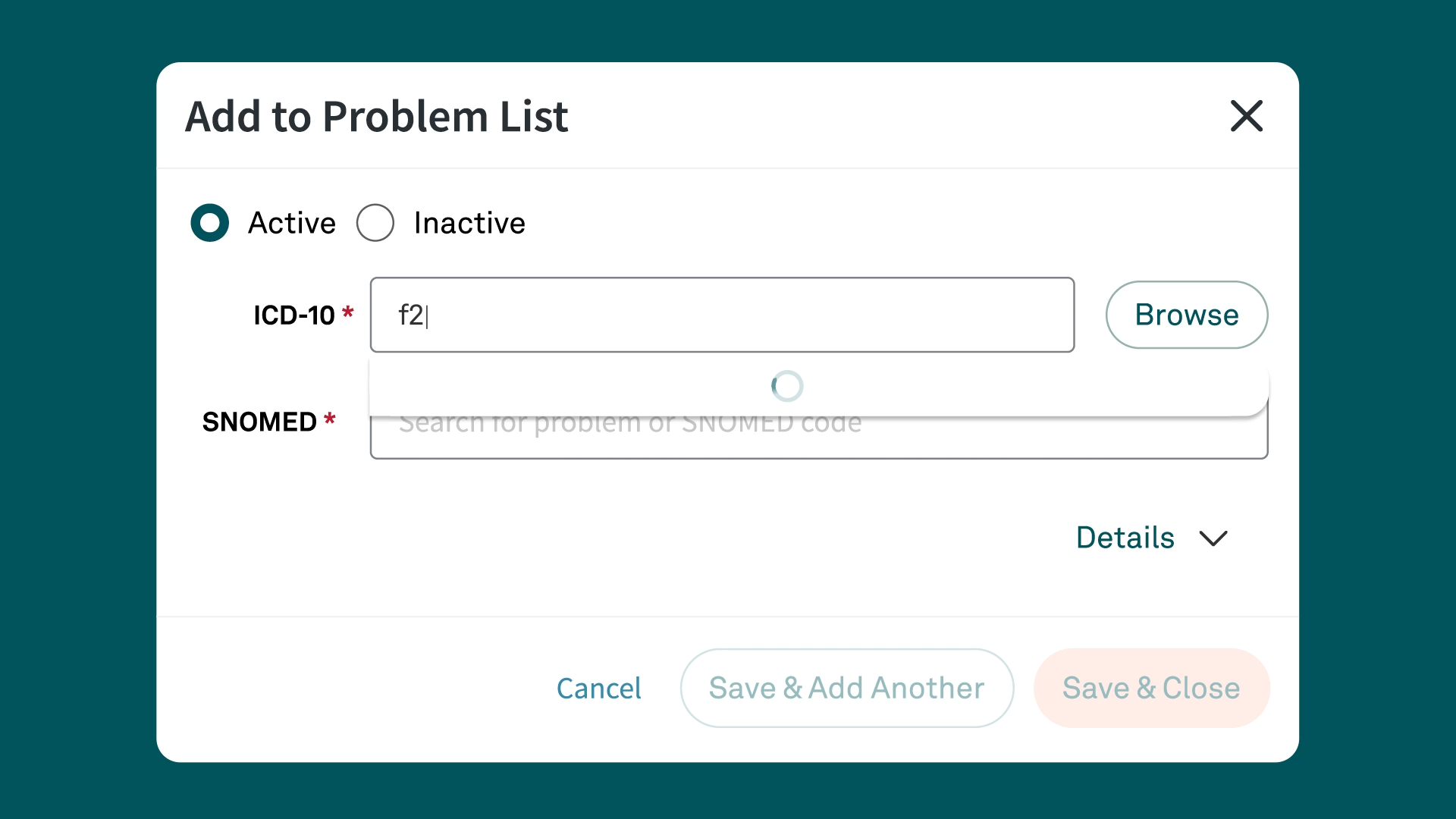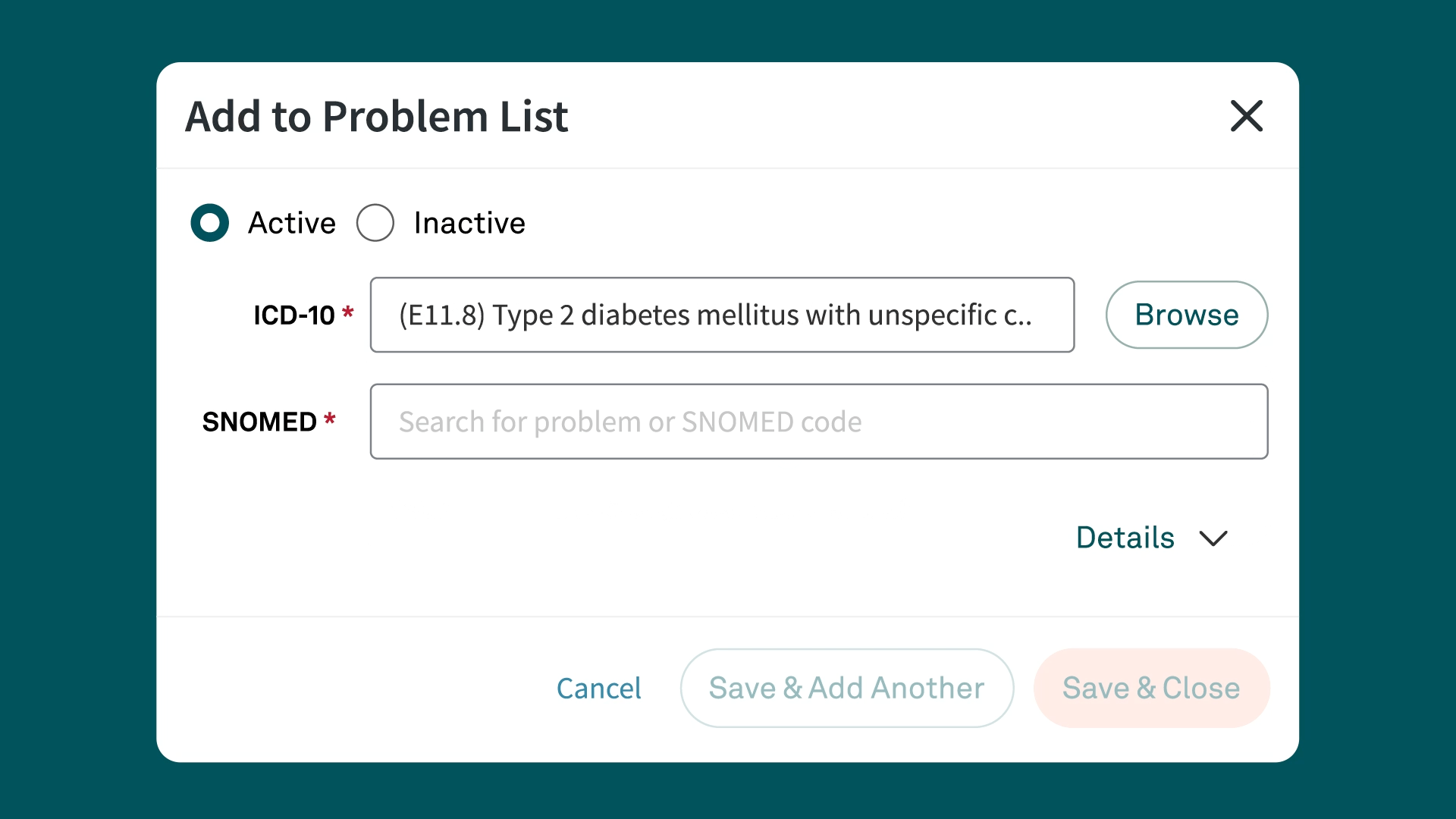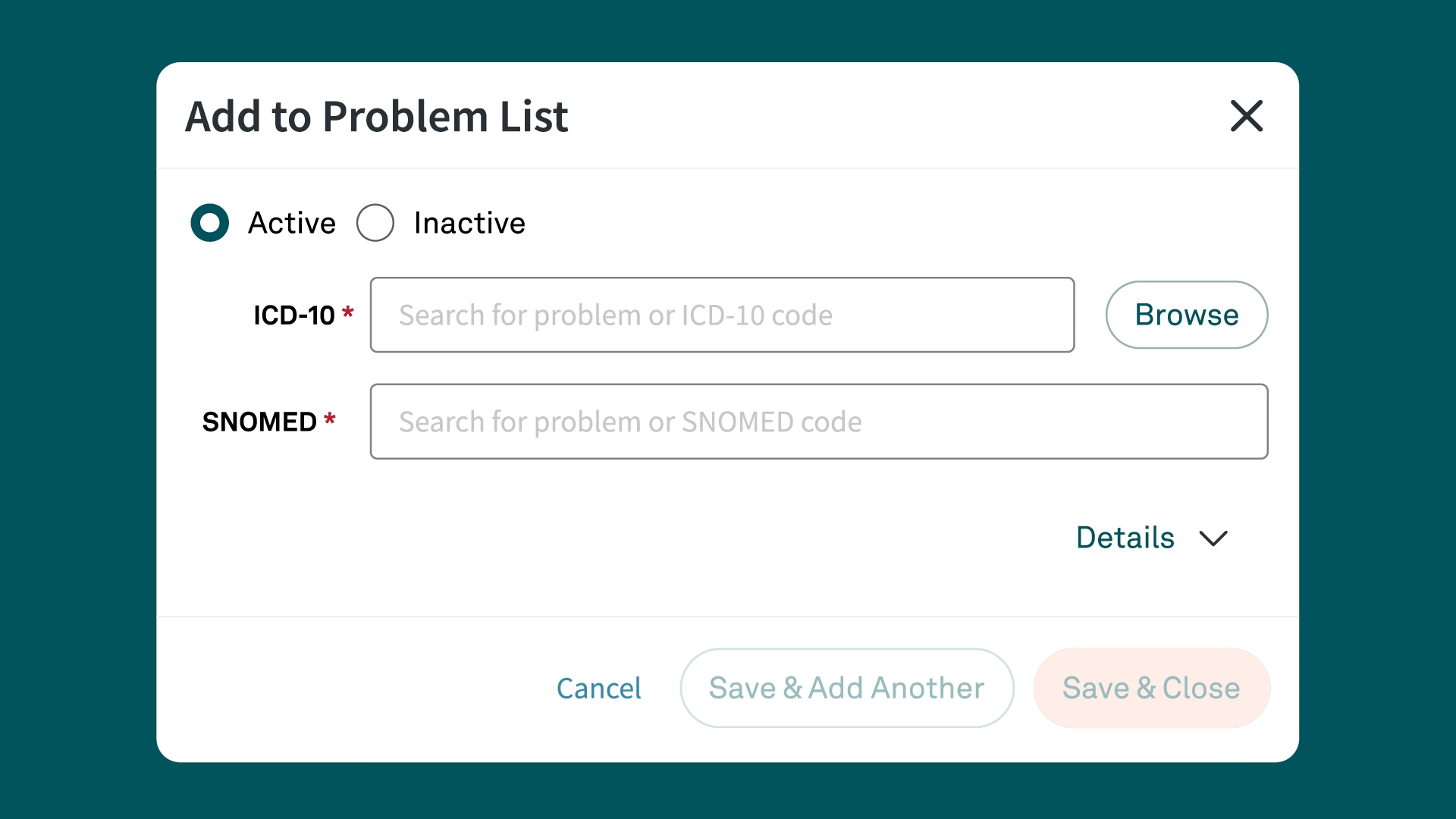
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Stay Ahead with Expert Healthcare & Billing Insights
Get the latest industry updates, financial tips, and expert strategies — delivered straight to your inbox.



