ICD-10 Code I48.19
Other persistent atrial fibrillation
What is the code I48.19?
ICD-10-CM code I48.19 is used to denote "other persistent atrial fibrillation." This code falls under the broader category of "I48" which pertains to "atrial fibrillation and flutter." Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common type of arrhythmia where the heart's upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly and out of coordination with the lower chambers (ventricles). The term “persistent” indicates that the arrhythmia lasts longer than 7 days and requires either pharmacologic or electrical intervention to restore normal rhythm.
Download your free resource now
Access it instantly — just complete the form

Detailed description of I48.19
I48.19 specifically identifies cases of atrial fibrillation that are persistent but have not been described as longstanding. Persistent atrial fibrillation can lead to various complications, including increased risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related issues. Persistent atrial fibrillation often requires medical intervention, such as medications, cardioversion, or ablation therapy, to manage and restore normal heart rhythm.
Symptoms commonly associated with I48.19
Patients with I48.19, or other persistent atrial fibrillation, may exhibit a range of symptoms, including:
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Anxiety
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may be intermittent or continuous. It’s important for healthcare providers to thoroughly assess these symptoms to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several ICD-10 codes are related to or similar to I48.19, including:
- I48.0: Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A type of atrial fibrillation that starts suddenly and stops on its own within 7 days
- I48.11: Longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation
- I48.20: Chronic atrial fibrillation, unspecified: Atrial fibrillation that is continuous and does not revert to normal rhythm
- I48.3: Typical atrial flutter: A regular, fast heartbeat originating from the atria
- I48.4: Atypical atrial flutter: A less common form of atrial flutter with different electrical pathways
Appropriate usage and guidelines for I48.19
When coding for I48.19, it is imperative to follow specific guidelines:
- Ensure that the diagnosis of persistent atrial fibrillation is well-documented in the patient's medical records
- Confirm that the atrial fibrillation does not fall into other specified categories such as paroxysmal
- I48.19 includes persistent atrial fibrillation described as chronic
- In cases involving multiple episodes of atrial fibrillation, the most recent and relevant type should be coded
Common pitfalls in coding with I48.19
Several common pitfalls can occur when coding for I48.19:
- Misclassifying the type of atrial fibrillation: Ensure that the AFib has not been specified to be a different type such as paroxysmal or further specified to be longstanding persistent AFib which requires a different code.
- Not following instructional notes: Do not assign I48.20 chronic atrial fibrillation, unspecified with I48.19. There is an excludes 1 note prohibiting the use of this code with I48.19. Assign only I48.19 for documentation of chronic persistent AFib.
- Incomplete documentation: Lack of detailed medical records can lead to inaccurate coding.
- Overlooking comorbid conditions: Other heart conditions or arrhythmias should be considered and coded appropriately.
Key resources for I48.19 coding
For accurate coding of I48.19, the following resources can be invaluable:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting: These guidelines provide comprehensive instructions for using ICD-10 codes.
- American Heart Association (AHA): Offers detailed information on atrial fibrillation, including diagnosis and management.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS offers a wealth of resources and updates on coding practices, including webinars, manuals, and bulletins.
- Professional coding organizations: Organizations like the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) offer educational resources, certifications, and support for medical coders.
- Coding reference books and software: Reference materials such as the ICD-10-CM codebook can support medical coders and providers.
These resources provide detailed instructions and updates on coding standards and practices.
Conclusion
ICD-10 code I48.19 is used to identify cases of "other persistent atrial fibrillation," a condition that requires careful medical management due to its potential complications. Accurate documentation and coding support effective patient care and appropriate reimbursement. Understanding the symptoms, related codes, and proper usage guidelines can help healthcare providers and coders ensure precise and efficient coding practices.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
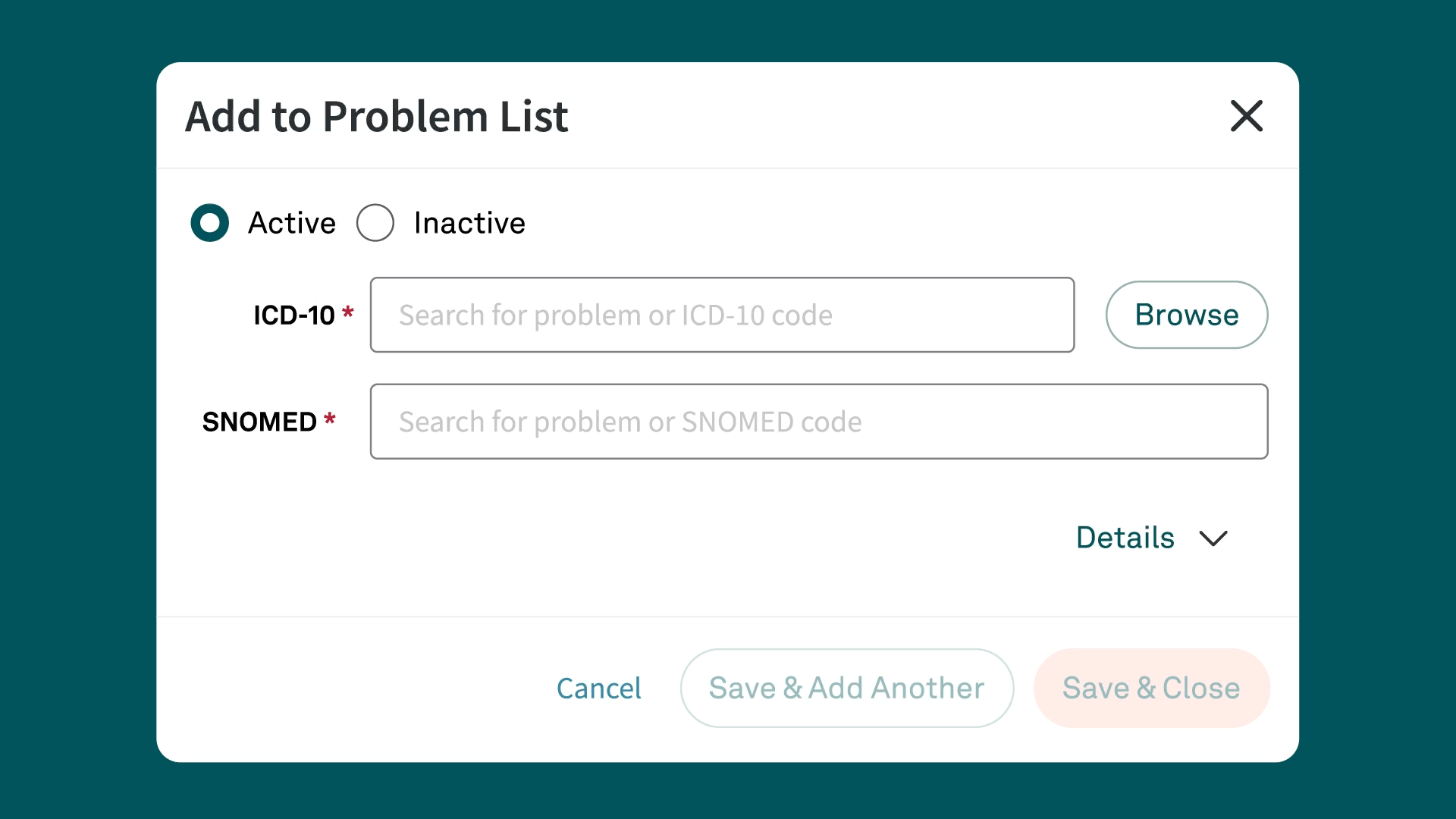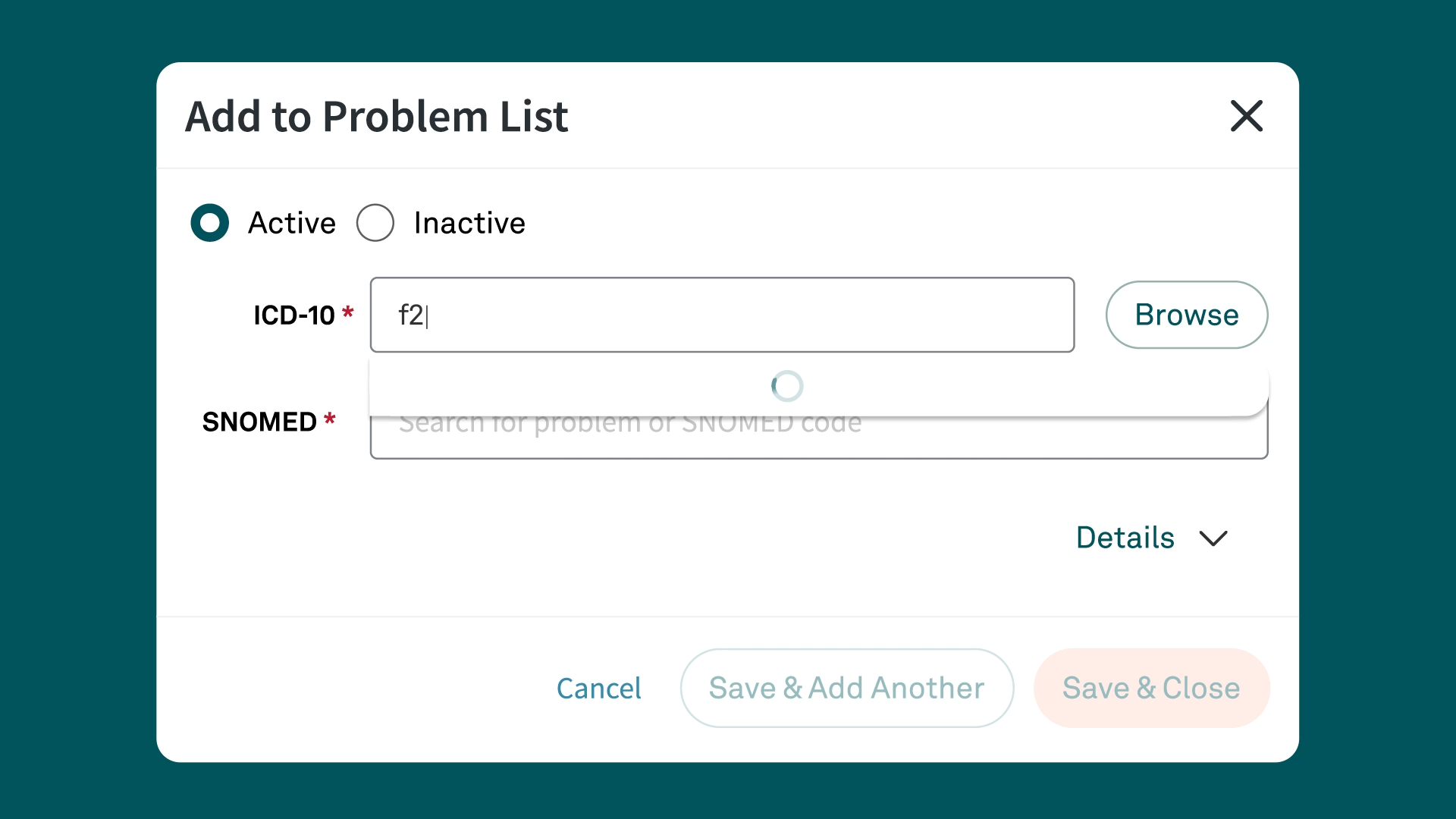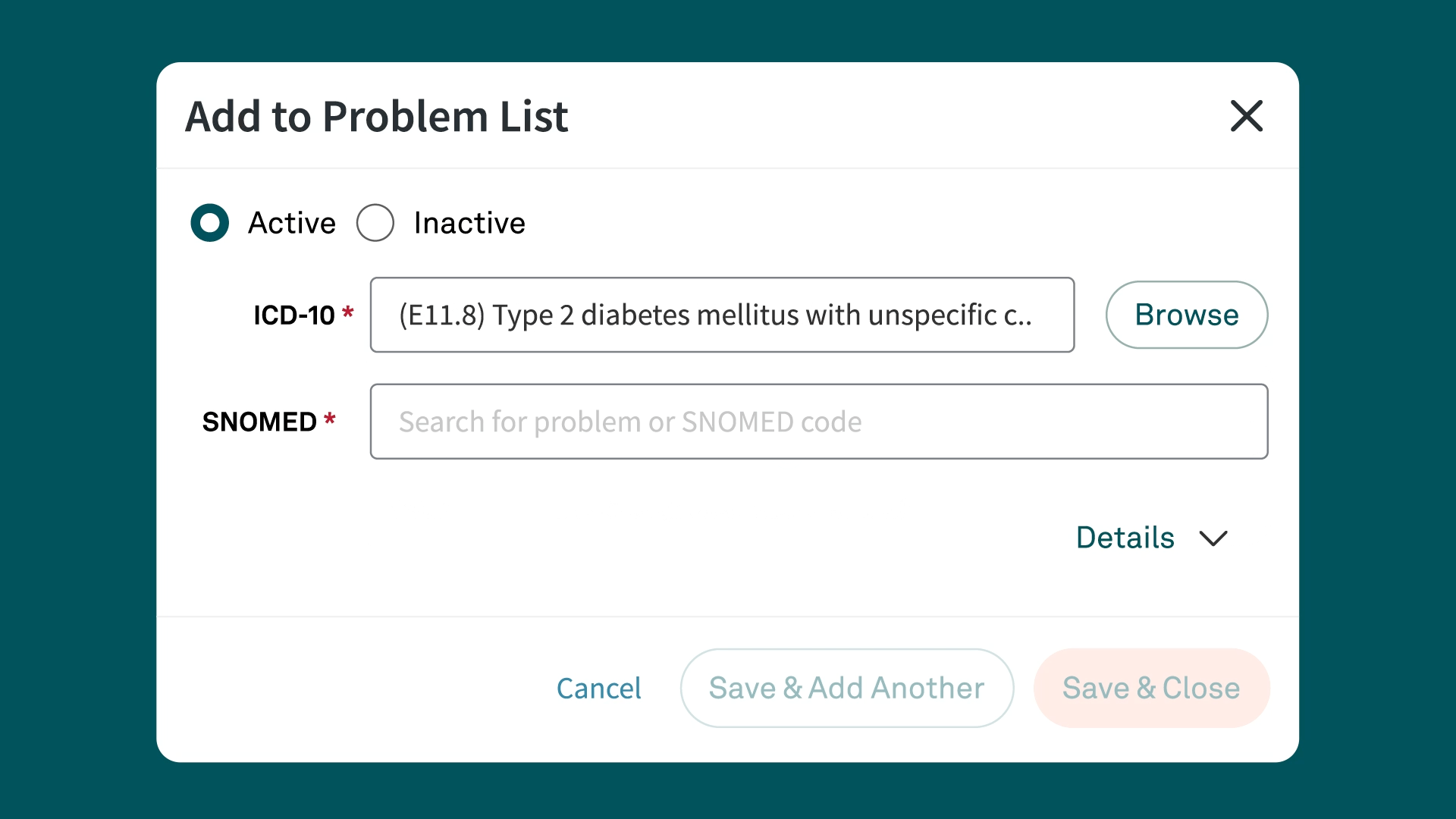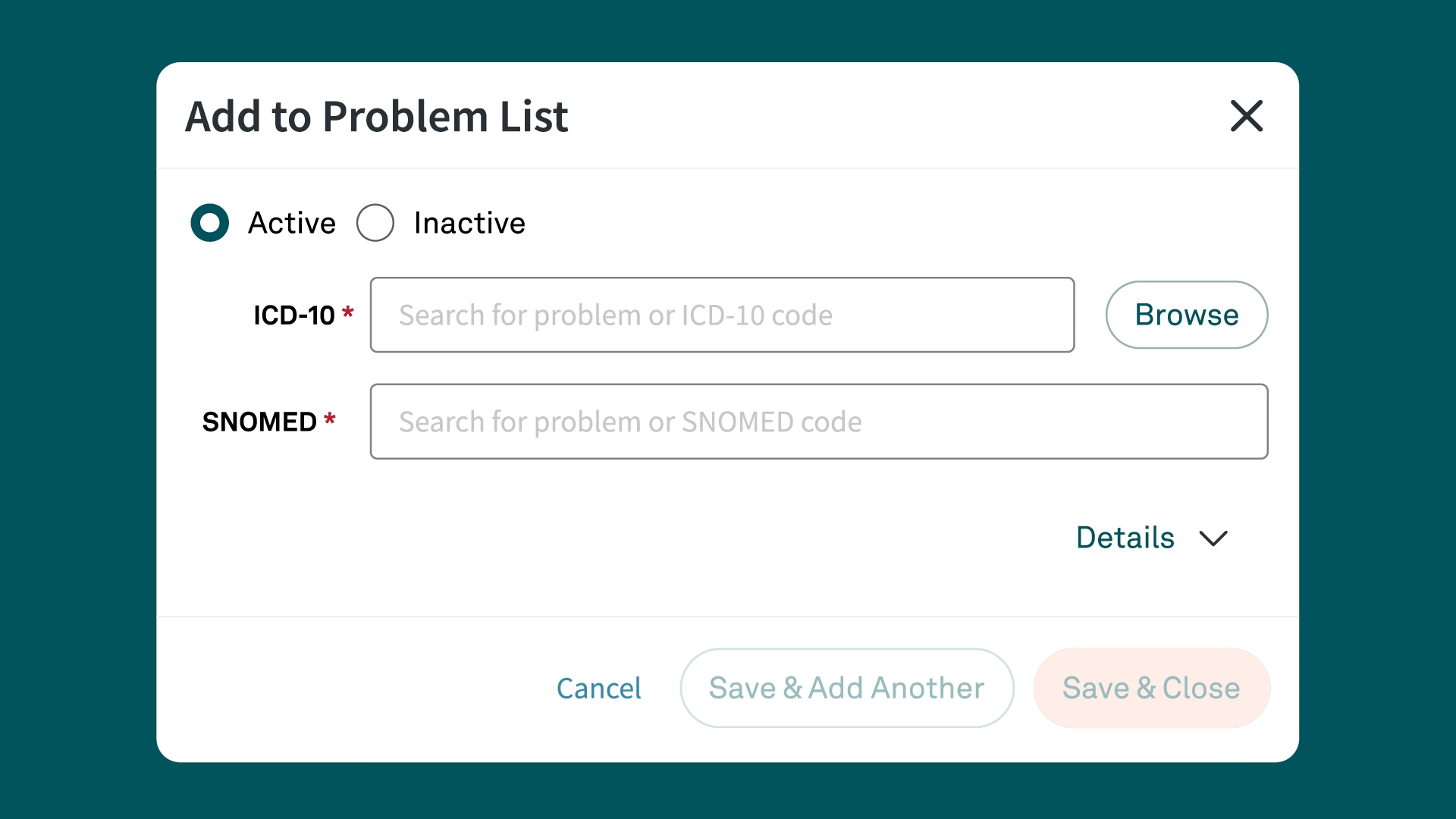
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Stay Ahead with Expert Healthcare & Billing Insights
Get the latest industry updates, financial tips, and expert strategies — delivered straight to your inbox.


