ICD-10 Code G62.9
Polyneuropathy, unspecified
What is the code G62.9?
The ICD-10-CM code G62.9 stands for "polyneuropathy, unspecified." This code is used by healthcare providers to indicate a diagnosis of polyneuropathy when the specific type is not identified. Polyneuropathy is a condition characterized by damage to multiple peripheral nerves, which can affect various parts of the body. The G62.9 code is used for accurate medical billing and documentation, ensuring that healthcare providers receive appropriate reimbursement for their services.
Detailed description of G62.9
Use ICD-10 code G62.9, "polyneuropathy, unspecified" in cases where a patient presents with symptoms of polyneuropathy, but the exact cause or type of neuropathy is not determined. Polyneuropathy involves widespread nerve damage that can lead to sensory and motor function impairments. This condition can result from a variety of causes, including diabetes, infections, toxins, and hereditary factors. The unspecified nature of G62.9 means that further diagnostic work may be necessary to pinpoint the underlying cause of the polyneuropathy.
Symptoms commonly associated with G62.9
Patients diagnosed with G62.9 may exhibit a range of symptoms, including:
- Numbness and tingling in the extremities
- Muscle weakness
- Burning or stabbing pain
- Sensitivity to touch
- Loss of coordination and balance
- Difficulty walking
- Muscle cramps or twitching
These symptoms can vary in severity and may affect different parts of the body, depending on the extent and location of the nerve damage.
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several other ICD-10 codes are related to G62.9 and may be used in similar contexts, including:
- G60.0: Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy
- G60.1: Refsum's disease
- G60.2: Neuropathy in association with hereditary ataxia
- G60.3: Idiopathic progressive neuropathy
- G61.0: Guillain-Barré syndrome
- G61.1: Serum neuropathy
- G61.8: Other inflammatory polyneuropathies
- G61.9: Inflammatory polyneuropathy, unspecified
- G62.0: Drug-induced polyneuropathy
- G62.1: Alcoholic polyneuropathy
- G62.2: Polyneuropathy due to other toxic agents
These codes provide more specific diagnoses and can help in identifying the exact nature of the neuropathy when further information is available.
Appropriate usage of G62.9 for billing
When using ICD-10 code G62.9 for billing purposes, it is important that the diagnosis of polyneuropathy is documented in the patient's medical records. The provider should be able to support the diagnosis with one of these clinical findings:
- Abducens nerve disorder
- Abducens neuropathy
- Aids with neuropathy (nerve disease)
- Aids with polyneuropathy (multiple nerve disease)
- Auditory neuropathy with dyssynchrony
- Auditory neuropathy/dyssynchrony
- Bilateral vestibular nerve disorder
- Both sides vestibular neuropathy
- Left auditory neuropathic dyssnchrony
- Left auditory neuropathic dyssynchrony
- Left vestibular neuropathy
- Neuropathy
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Neuropathy (nerve damage), peripheral
- Neuropathy (nerve damage), peripheral axonal nerve
- Neuropathy due to human immunodeficiency virus
- Peripheral axonal neuropathy
- Peripheral nerve disease
- Polyneuropathy
- Polyneuropathy (multiple nerve disorder)
- Polyneuropathy associated with aids
- Right auditory neuropathic dyssynchrony
- Right vestibular neuropathy
The use of G62.9 is appropriate when the provider cannot determine the type of polyneuropathy despite thorough evaluation.
Instructional notes and/or guidelines with G62.9
When coding for G62.9, follow these instructional notes and guidelines:
- Clearly document the diagnosis of polyneuropathy in the patient's medical record.
- Use G62.9 only when the specific type or cause of polyneuropathy is not identified.
- Avoid using G62.9 if a more specific code is applicable based on the available clinical information.
- Be sure to include symptom documentation.
Common pitfalls in coding with G62.9
Some common pitfalls to be aware of when coding with G62.9 include:
- Using G62.9 when a more specific diagnosis code is available and applicable.
- Failing to show that the unspecified code is appropriate and that a code with more specificity does not exist.
- Overlooking the need for further diagnostic testing to identify the specific type or cause of polyneuropathy.
- Misinterpreting symptoms that may be indicative of other conditions leading to incorrect coding.
Key resources for G62.9 coding
Healthcare professionals can access several key resources to accurately code G62.9, including:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting: These guidelines provide comprehensive instructions on the use of ICD-10 codes.
- American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA): AHIMA provides education, certification, and resources for medical coders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS offers a wealth of resources and updates on coding practices, including webinars, manuals, and bulletins.
- Professional coding organizations: Organizations such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) offer training, certification, and resources for medical coders.
- Professional coding reference books and software: Reference materials can support medical coders and providers.
These resources provide comprehensive guidance and updates on coding practices to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Conclusion
The ICD-10-CM code G62.9, "polyneuropathy, unspecified," is used to diagnose and document cases of polyneuropathy when the specific type is not determined. Proper usage of this code requires documentation and adherence to coding guidelines. By understanding the symptoms, related codes, and common pitfalls associated with G62.9, healthcare professionals can help ensure accurate billing and effective patient care. Using key resources and staying informed about coding practices will further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical coding and billing processes.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
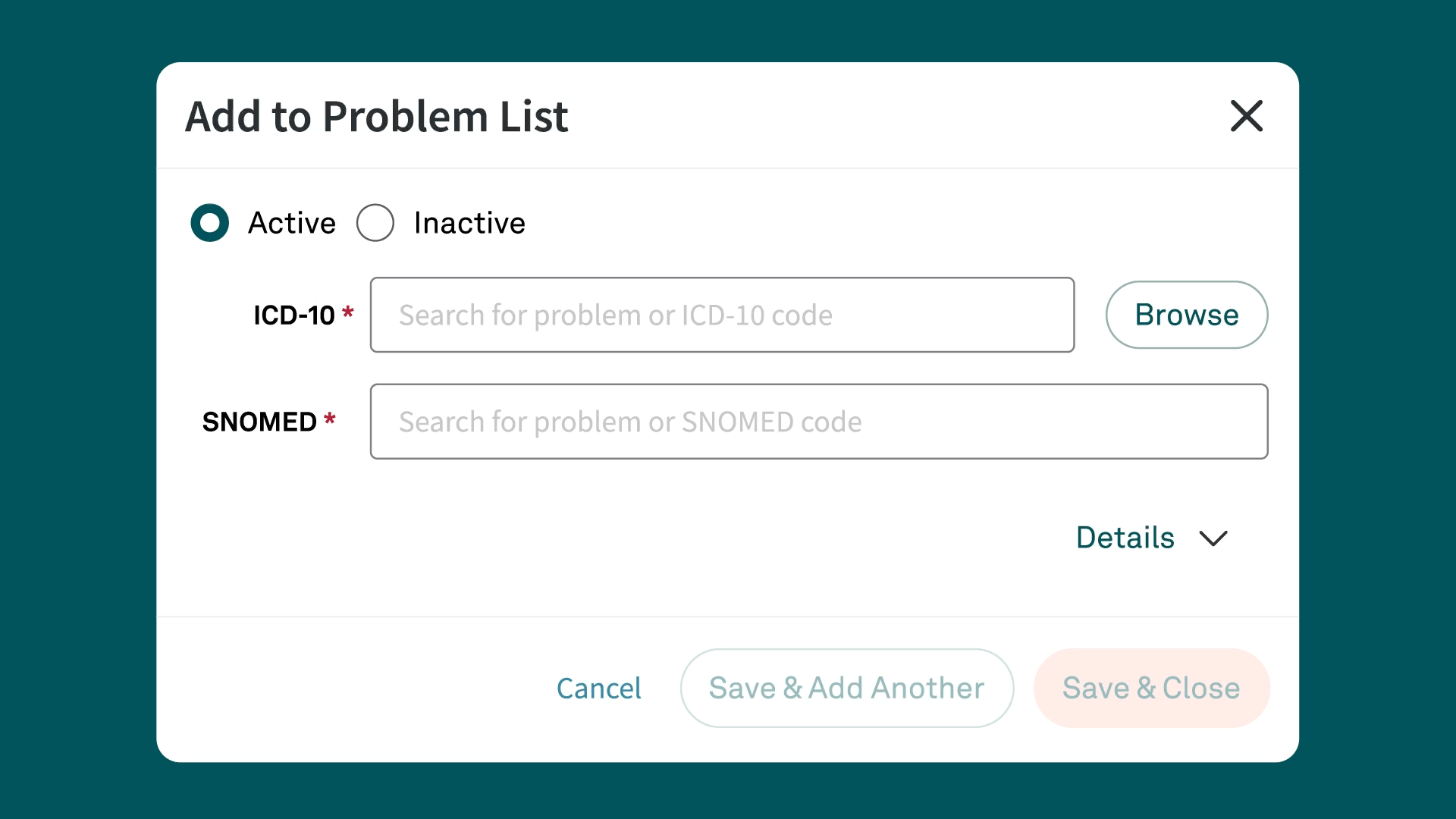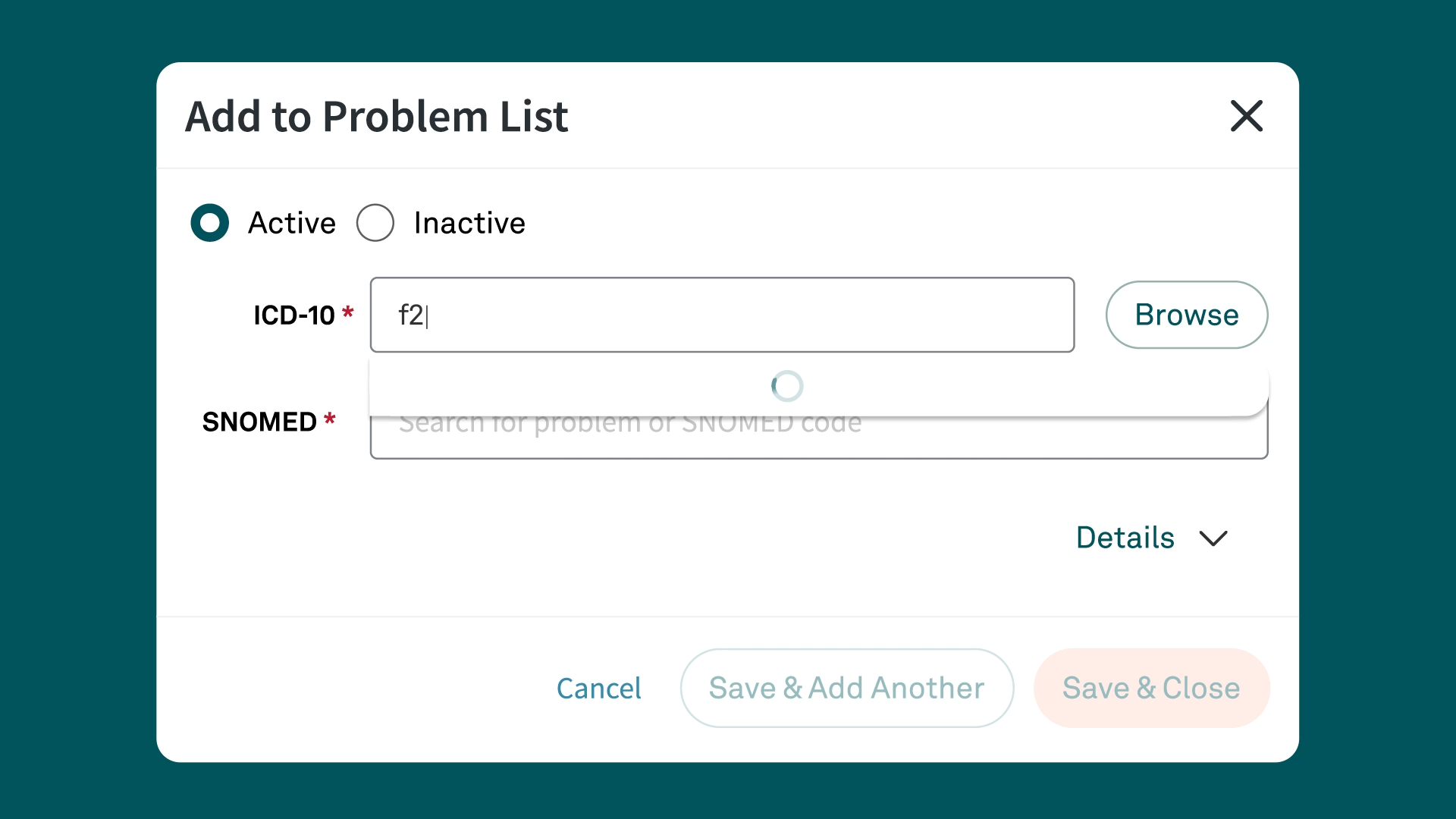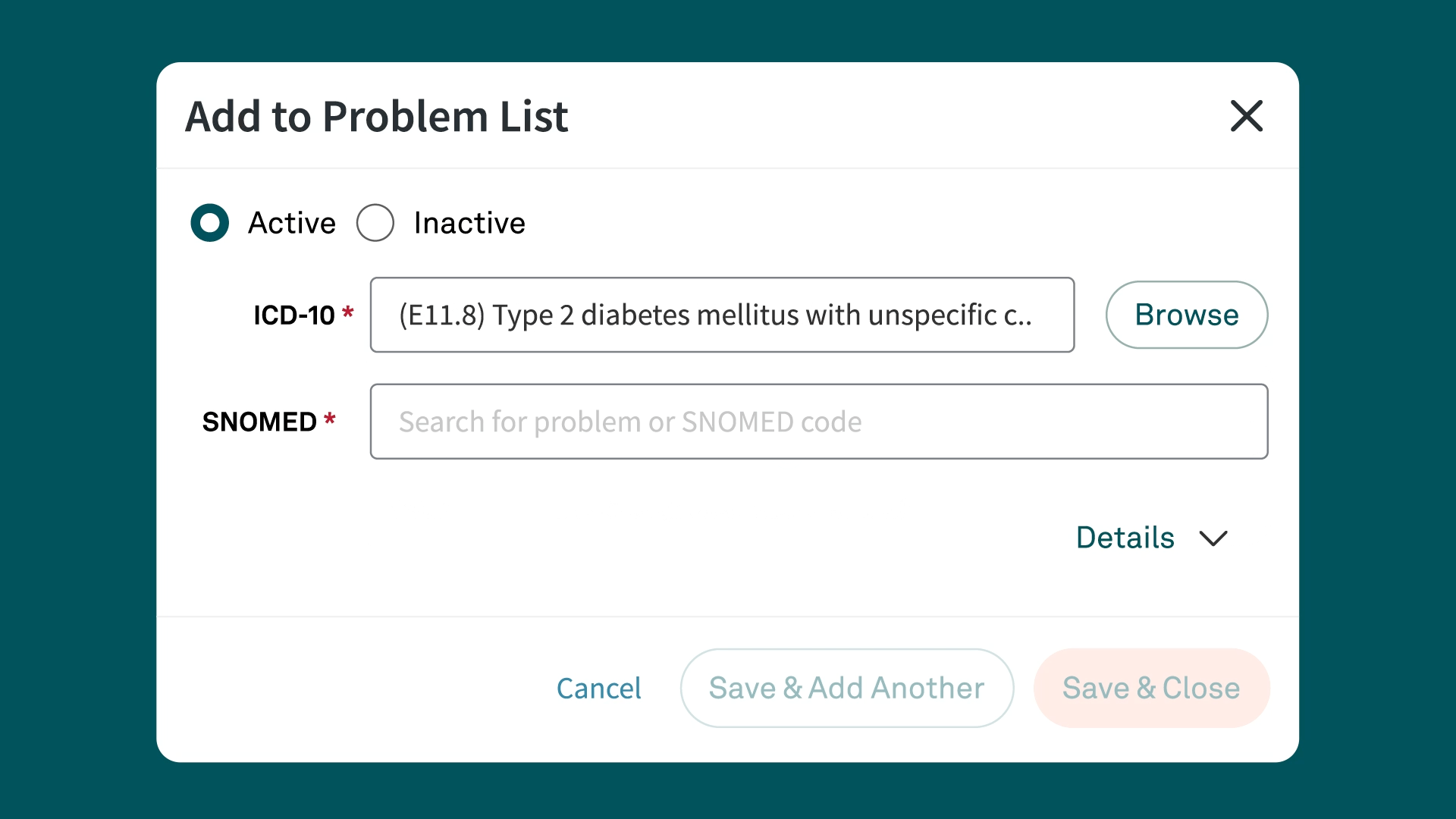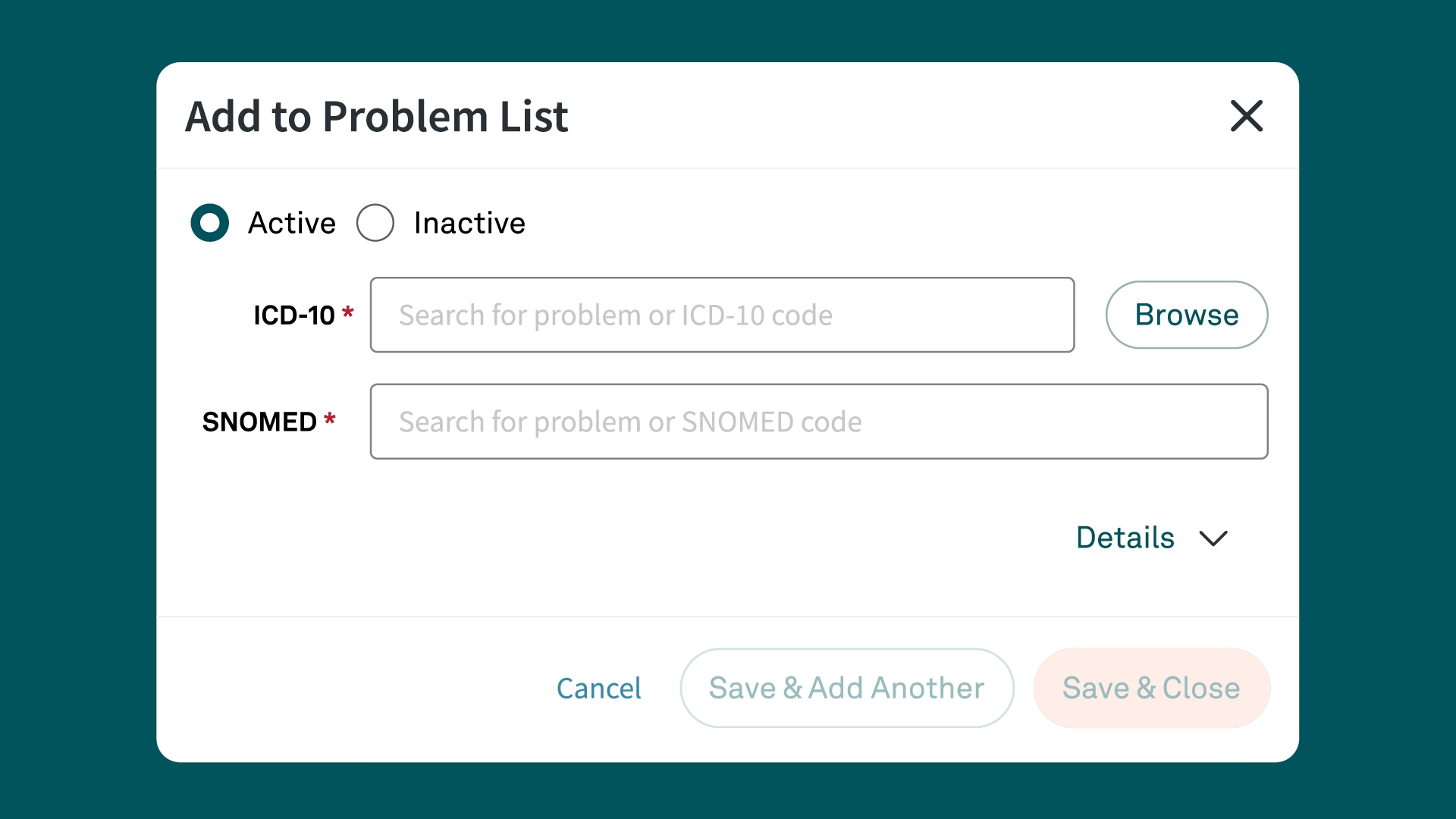
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Subscribe to The Intake:
A weekly check-up for your independent practice



