ICD-10 Code E11.69
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication
What is the code E11.69?
The ICD-10-CM code E11.69 refers to "Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication." This code is used by healthcare providers and medical coders to document and bill cases in which a patient with Type 2 diabetes mellitus presents with complications that do not fall into more specific categories. This code is essential for capturing the complexity of diabetes management and ensuring appropriate reimbursement for care provided.
Detailed description of E11.69
E11.69 is a specific code within the ICD-10 classification system that falls under the broader category of codes for diabetes mellitus. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. The "other specified complication" component of this code indicates that the patient has a complication related to their diabetes that is not classified under more specific codes, such as kidney complications, eye complications, or neuropathy. These unspecified complications could include a wide range of issues that are directly related to the patient's diabetes but do not have a dedicated ICD-10 code.
Symptoms commonly associated with E11.69
Patients diagnosed with E11.69 may present with a variety of symptoms depending on the specific complication associated with their Type 2 diabetes. Common symptoms could include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Frequent urination and increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
The exact symptoms will vary based on the nature of the unspecified complication, but they are generally related to the metabolic dysfunction caused by diabetes.
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several other ICD-10 codes are closely related to E11.69. These include:
- E11.21: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy
- E11.22: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic chronic kidney disease
- E11.40: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic neuropathy, unspecified
- E11.51: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic peripheral angiopathy without gangrene
- E11.641: Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypoglycemia with coma
These related codes specify particular complications associated with Type 2 diabetes, whereas E11.69 is used when the complication does not fit into these more specific categories.
Appropriate usage of E11.69 for billing
When using the E11.69 code for billing purposes, it is essential to ensure that the patient's medical records provide documentation of the unspecified complication related to their Type 2 diabetes mellitus. The use of this code should reflect a diagnosis that confirms the presence of a complication that is directly attributable to the patient's diabetes but does not fall under a more specific ICD-10 code.
Billing with E11.69 typically involves the following steps:
1. Diagnosis: Confirm that the complication is related to Type 2 diabetes mellitus and does not fit into other specific diabetic complication codes.
2. Documentation: Ensure that the patient's medical records include documentation of the diagnosis.
3. Coding: Use the E11.69 code in conjunction with other relevant codes to accurately reflect the patient's condition and the care provided. Use additional codes to identify control using:
- Insulin (Z79.4)
- Oral antidiabetic drugs (Z79.84)
- Oral hypoglycemic drugs (Z79.84)
Instructional notes and/or guidelines with E11.69
When coding with E11.69, it is important to follow specific guidelines to ensure accurate and compliant billing. These guidelines include:
- Combination coding: E11.69 can be used in combination with other codes to fully capture the patient's condition. For example, coding for the primary diabetes diagnosis alongside E11.69 can provide a clearer picture of the patient's health status.
- Documentation: The patient's medical records should clearly describe the unspecified complication and its relation to the patient's Type 2 diabetes.
- Regular updates: Stay informed about updates to ICD-10 codes and guidelines to ensure ongoing compliance and accuracy in coding practices.
Common pitfalls in coding with E11.69
Several common pitfalls can occur when coding with E11.69:
- Lack of specificity: Using E11.69 when a more specific code is available can lead to inaccurate coding. Always verify that no more specific code applies before using E11.69.
- Inadequate documentation: Use of the E11.69 code in cases where documentation does not adequately support its application may result in claim denials.
- Misinterpretation of guidelines: Misunderstanding the guidelines for using E11.69 can lead to incorrect coding. Regular training and updates on coding practices can help mitigate this risk.
- Overuse of unspecified codes: Over-reliance on unspecified codes like E11.69 can indicate a lack of thorough assessment. Strive to use the most specific codes available whenever possible.
Key resources for E11.69 coding
To stay informed and accurate in coding with E11.69, healthcare providers and medical coders can rely on several key resources:
- ICD-10 Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting: These guidelines provide comprehensive instructions on the use of ICD-10 codes, including E11.69.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS offers a wealth of resources and updates on coding practices, including webinars, manuals, and bulletins.
- American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA): AHIMA provides education, certification, and resources for medical coders, including specific guidance on diabetes-related codes.
- Professional coding organizations: Organizations such as the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) offer training, certification, and resources for medical coders.
Conclusion
The ICD-10-CM code E11.69, "Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other specified complication," captures the complexity of diabetes management when complications do not fall into more specific categories. Accurate usage of this code requires detailed documentation, a determination that the patient’s condition does not fit into another diabetic complication code, and adherence to coding guidelines.
By understanding the appropriate use and potential pitfalls of E11.69, healthcare providers and medical coders can help ensure accurate billing and effective patient care documentation. Leveraging key resources and staying updated on coding practices can further enhance the accuracy and compliance of medical coding efforts.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
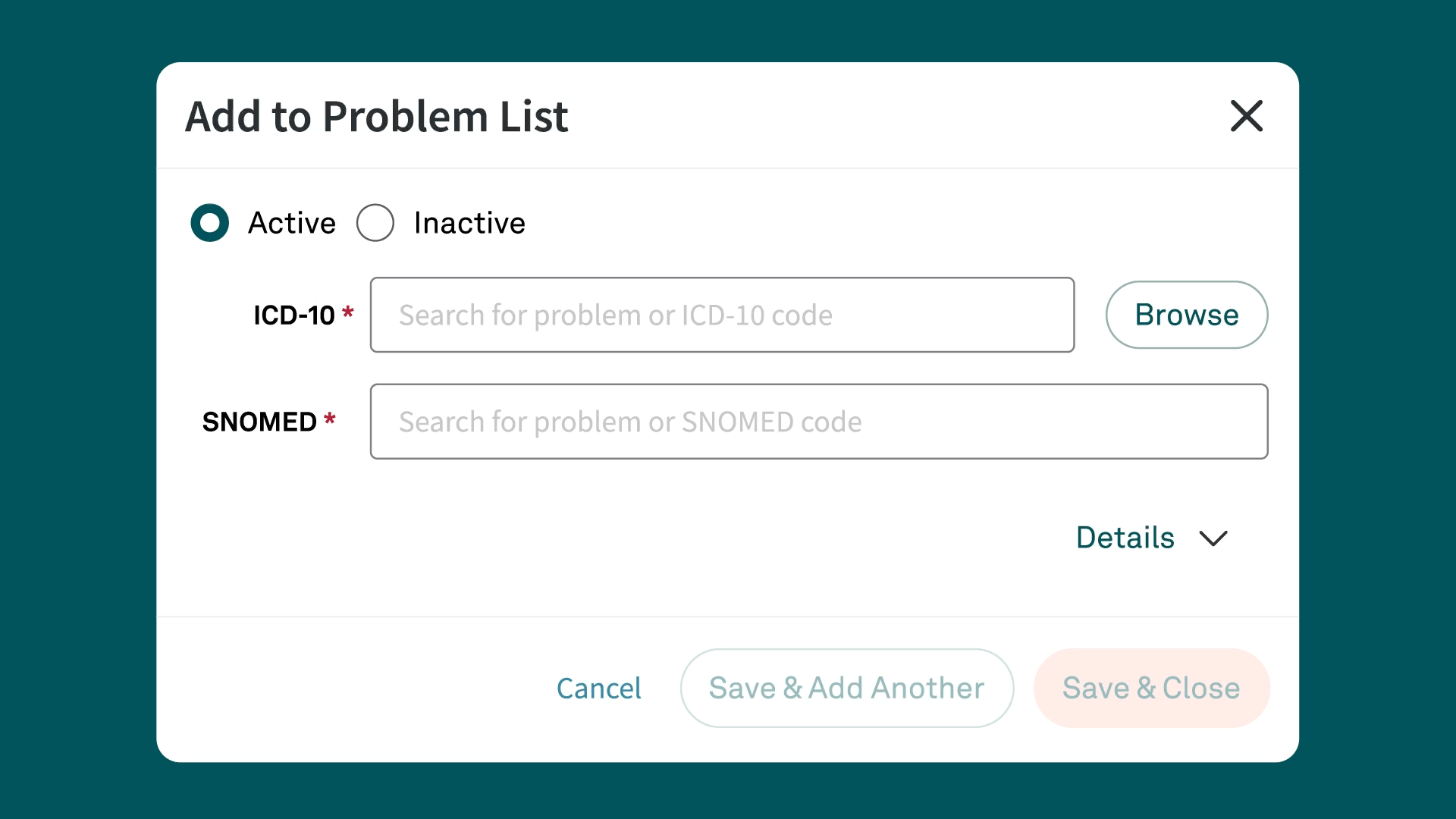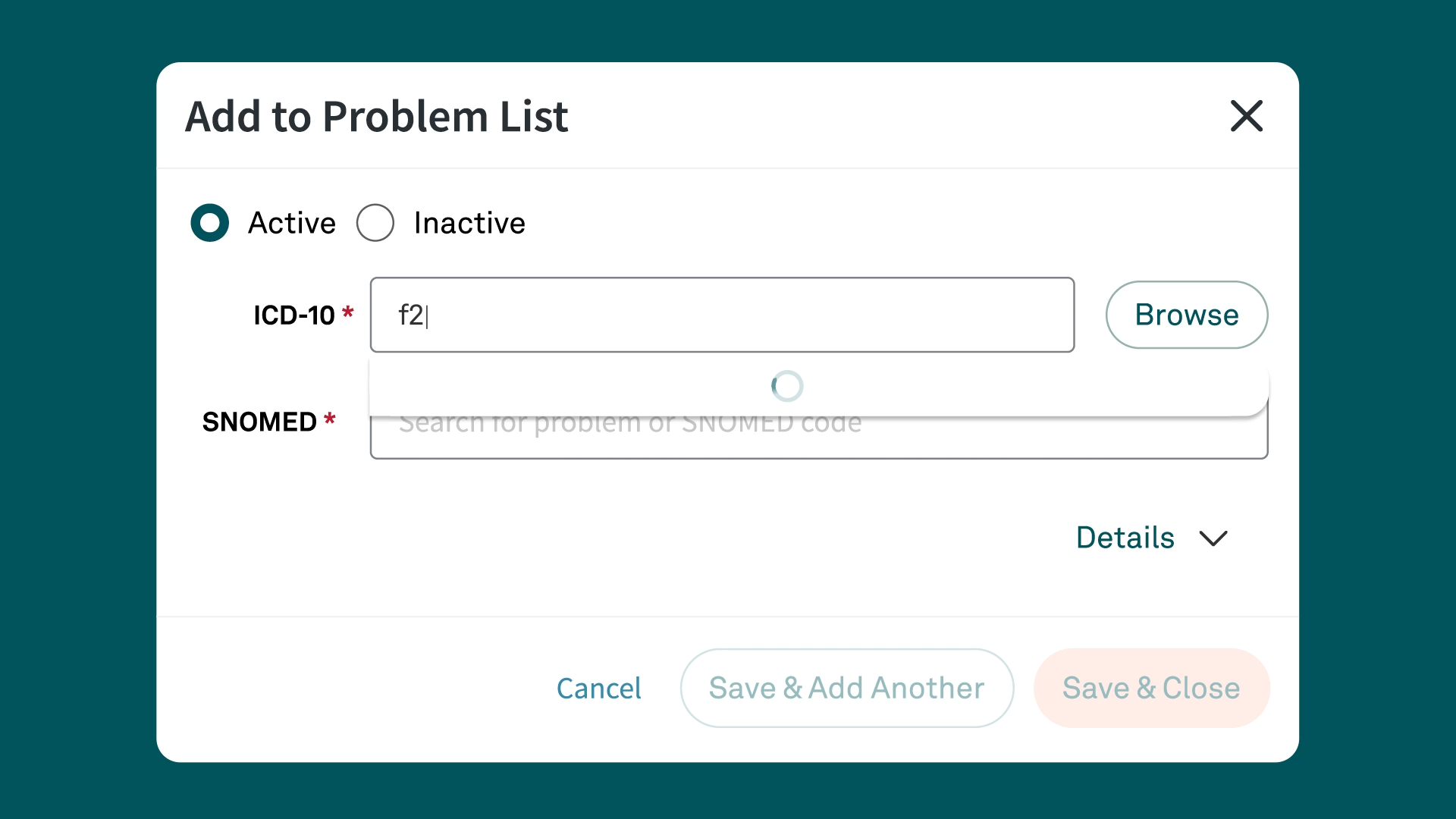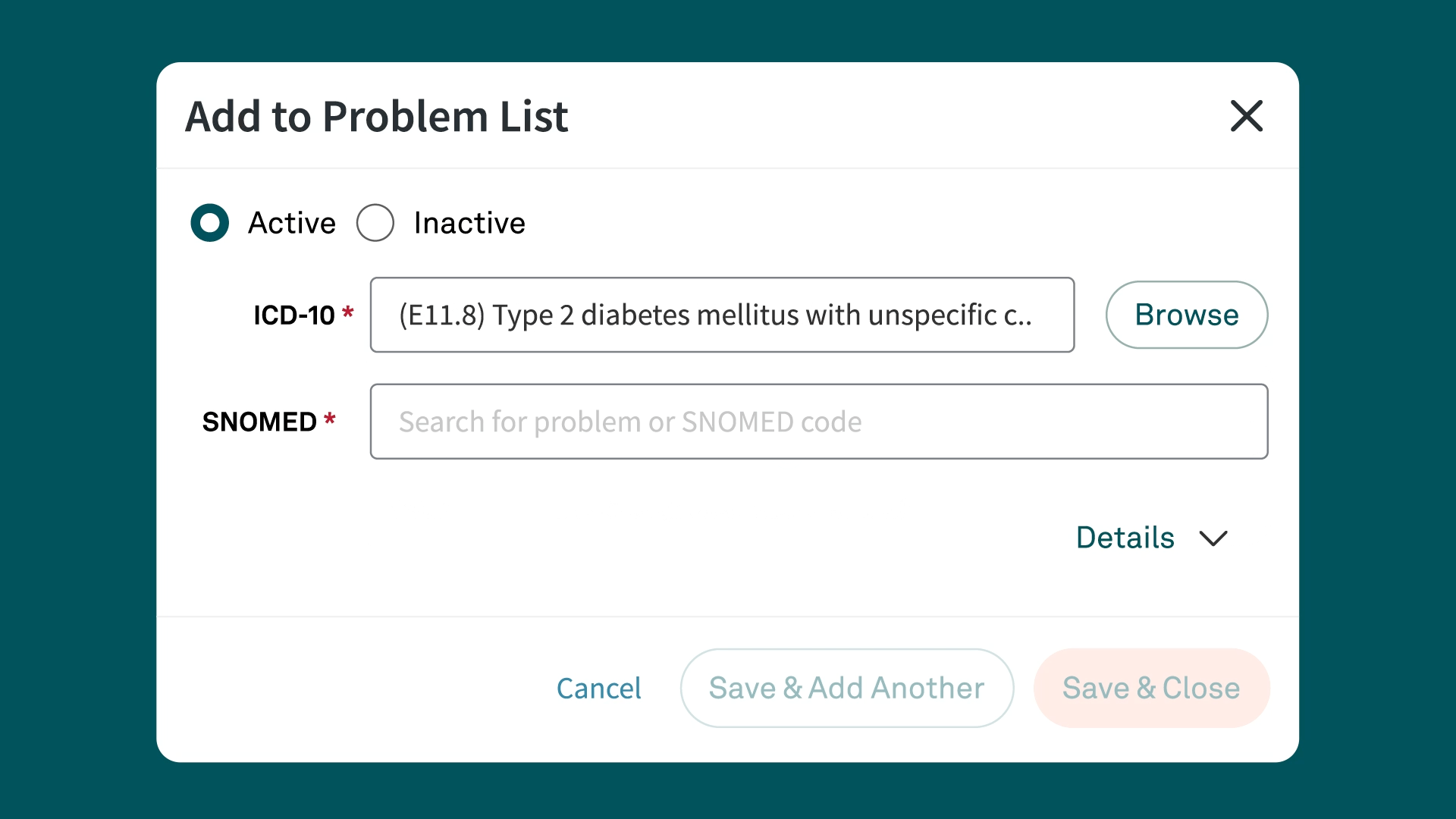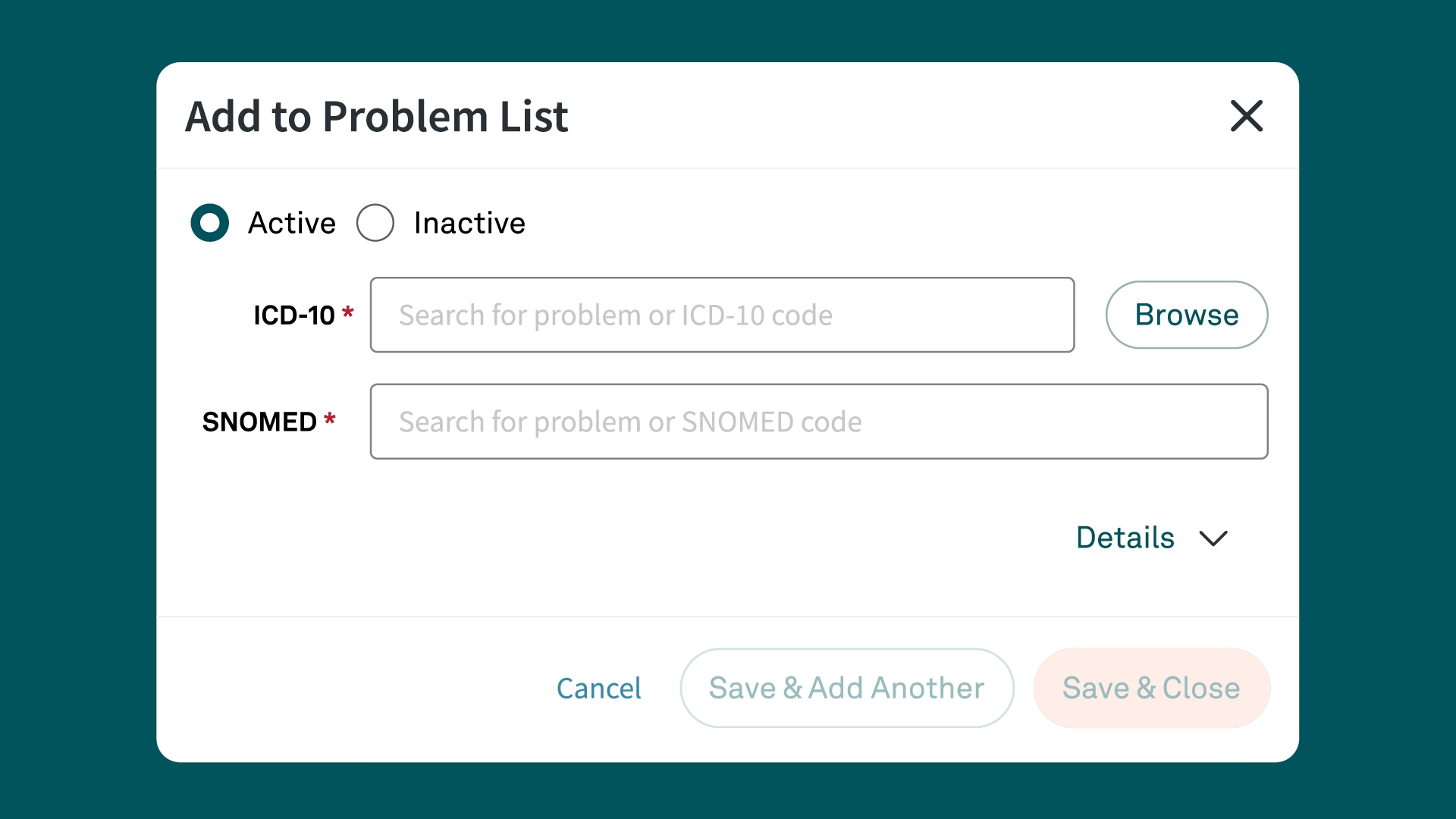
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Stay Ahead with Expert Healthcare & Billing Insights
Get the latest industry updates, financial tips, and expert strategies — delivered straight to your inbox.



