ICD-10 Code B18.3
Chronic viral hepatitis C
What is the code B18.2?
B18.2 is the ICD-10 code used to identify chronic viral hepatitis C. Healthcare providers use this code to document a patient's diagnosis of a chronic infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV).
Detailed description of B18.2
Chronic viral hepatitis C, coded as B18.2, refers to a long-term infection with the hepatitis C virus. This condition is characterized by the presence of the virus in the bloodstream for more than 6 months. Chronic hepatitis C can lead to significant liver damage, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma if left untreated.
Symptoms commonly associated with B18.2
Patients with chronic hepatitis C (B18.2) may often be asymptomatic, especially in the early stages of the infection. However, as the disease progresses, common symptoms can include:
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Joint pain
Related and similar ICD-10 codes
Several ICD-10 codes are related or similar to B18.2:
- B18.0: Chronic viral hepatitis B with delta-agent
- B18.1: Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent
- B18.8: Other chronic viral hepatitis
- B18.9: Chronic viral hepatitis, unspecified
- B19.20: Unspecified viral hepatitis C without hepatic coma
Appropriate usage and guidelines for B18.2
When coding for chronic viral hepatitis C using B18.2, ensure that provider documentation indicates that the chronic viral hepatitis C or its treatment affected patient care and management for the current encounter.
Another term that may be coded with B18.2 is carrier of viral hepatitis C. It's also important to note that B18.2 should not be used for acute hepatitis C infections; instead, use the appropriate acute hepatitis C code. Additionally, if the patient has cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma due to chronic hepatitis C, code these conditions separately.
Common pitfalls in coding with B18.2
Several common pitfalls can occur when coding B18.2:
- Incorrect duration: Using B18.2 for patients who have been diagnosed with acute viral hepatitis C.
- Lack of documentation: Failing to provide sufficient documentation regarding acuity of the condition.
- Ignoring comorbidities: Not coding additional conditions such as cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma when present.
- Using unspecified codes: Overreliance on unspecified codes like B18.9 when a more specific code like B18.2 is applicable.
Key resources for B18.2 coding
To ensure accurate coding for B18.2, consider the following resources:
- ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting: These guidelines provide comprehensive instructions for using ICD-10 codes.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS offers a wealth of resources and updates on coding practices, including webinars, manuals, and bulletins.
- Professional coding organizations: Organizations like the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) and the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) offer educational resources, certifications, and support for medical coders.
- Coding reference books and software: Reference materials such as the ICD-10-CM codebook can support medical coders and providers.
These resources provide comprehensive guidelines and updates on ICD-10 coding practices and can help ensure accurate and compliant coding.
Conclusion
ICD-10 code B18.2 is used to document chronic viral hepatitis C, a condition that can have significant implications for a patient's health. Accurate coding helps ensure proper documentation, treatment planning, and billing. By understanding the detailed description, associated symptoms, related codes, and common pitfalls, healthcare providers can ensure they are using B18.2 correctly and effectively. Accessing key resources and staying updated on coding guidelines can further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical coding practices.
Simplify ICD-10 code documentation with Tebra
Tebra’s EHR+ gives you quick searches and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) field names for efficient code documentation. Plus, Tebra automatically saves ICD-10 to SNOMED mapping for future searches, streamlining your workflow.
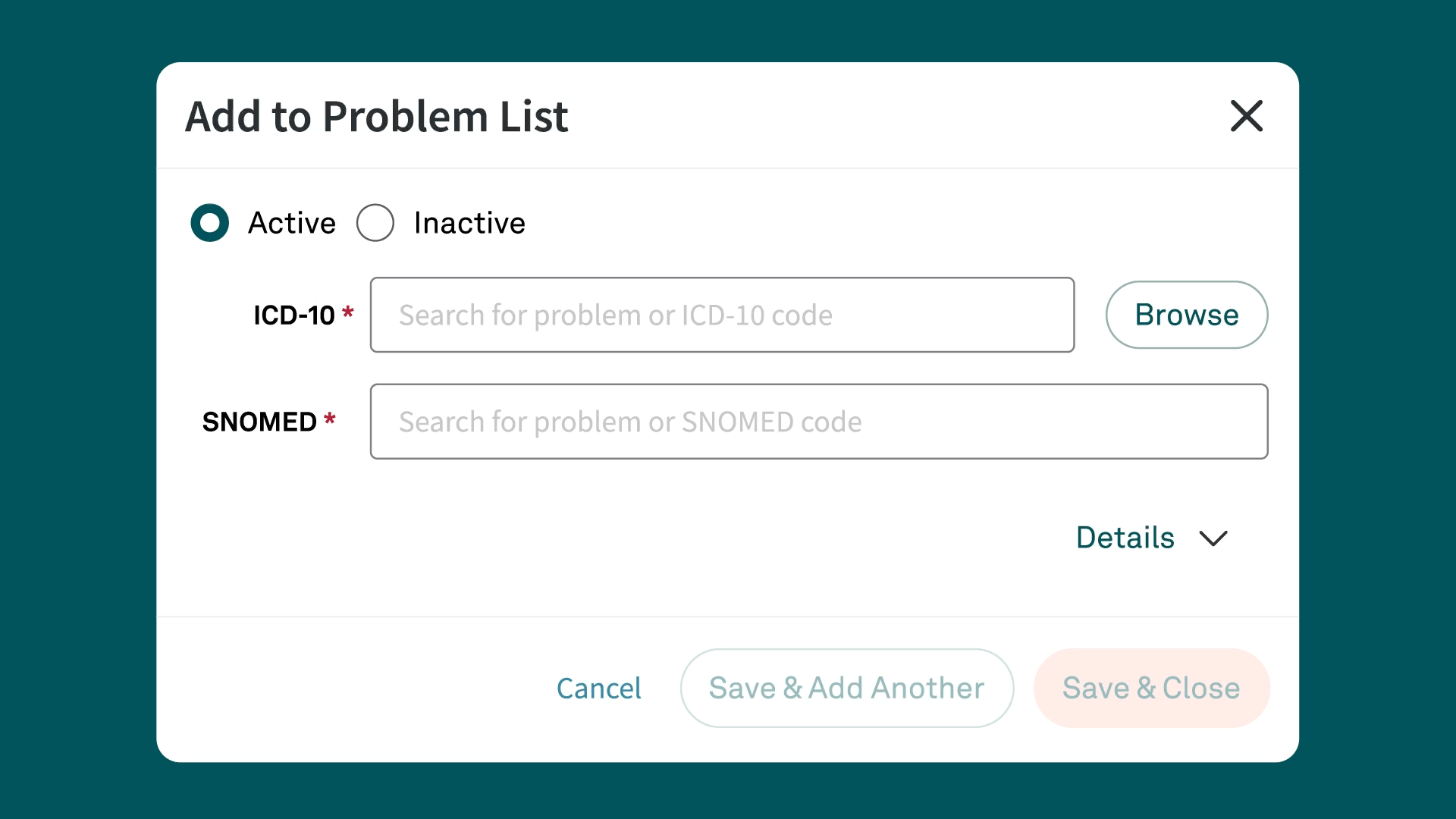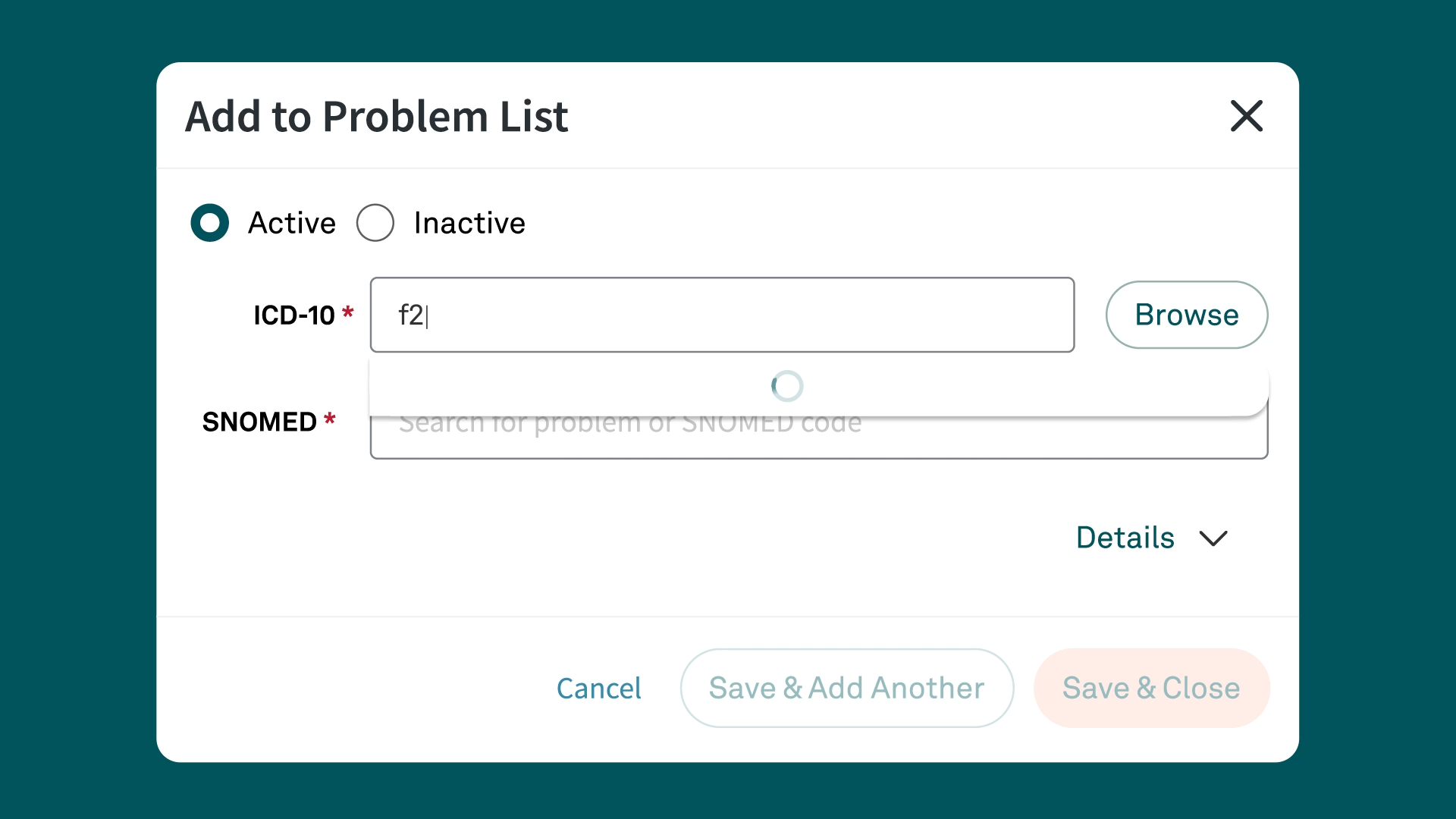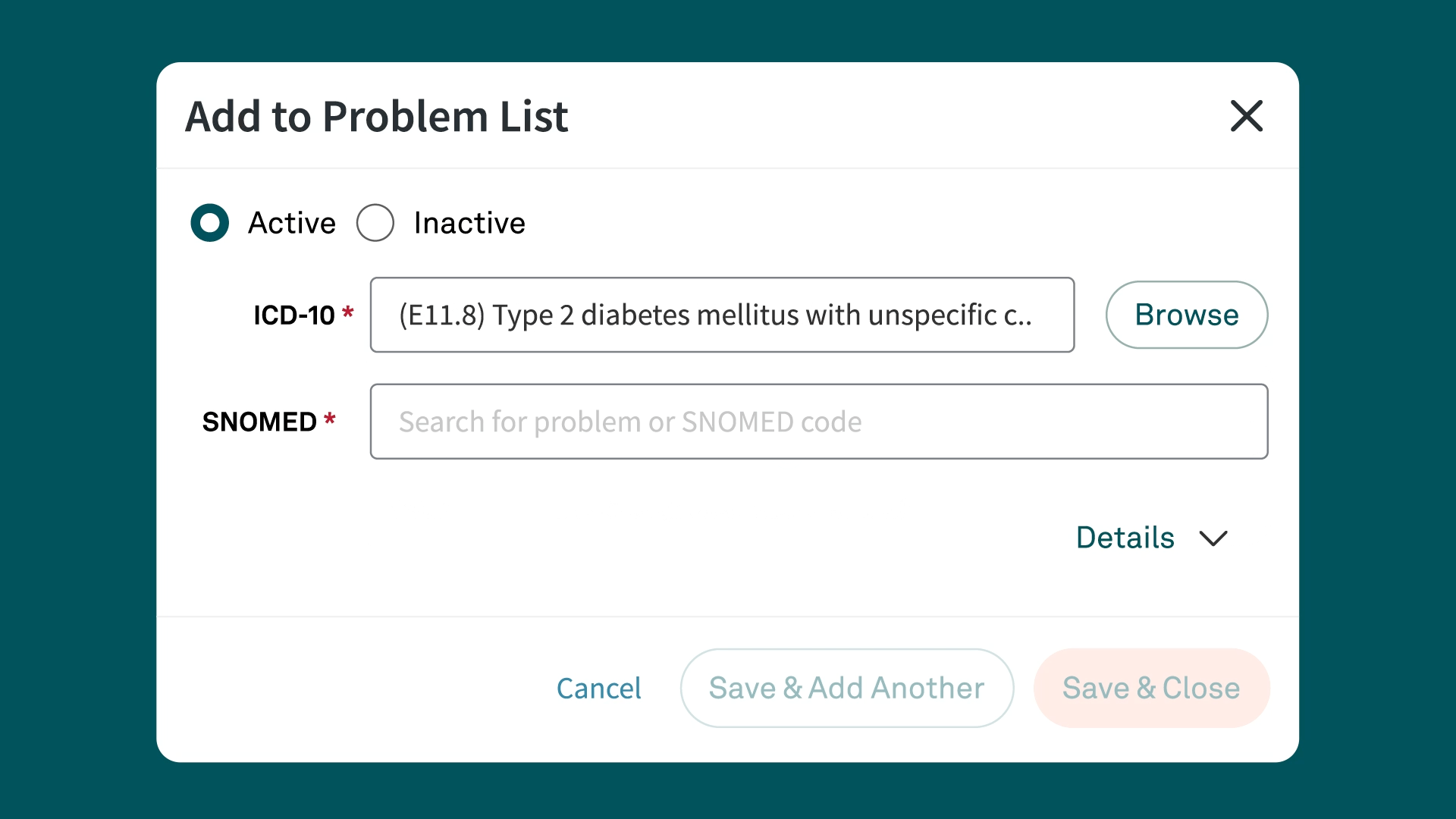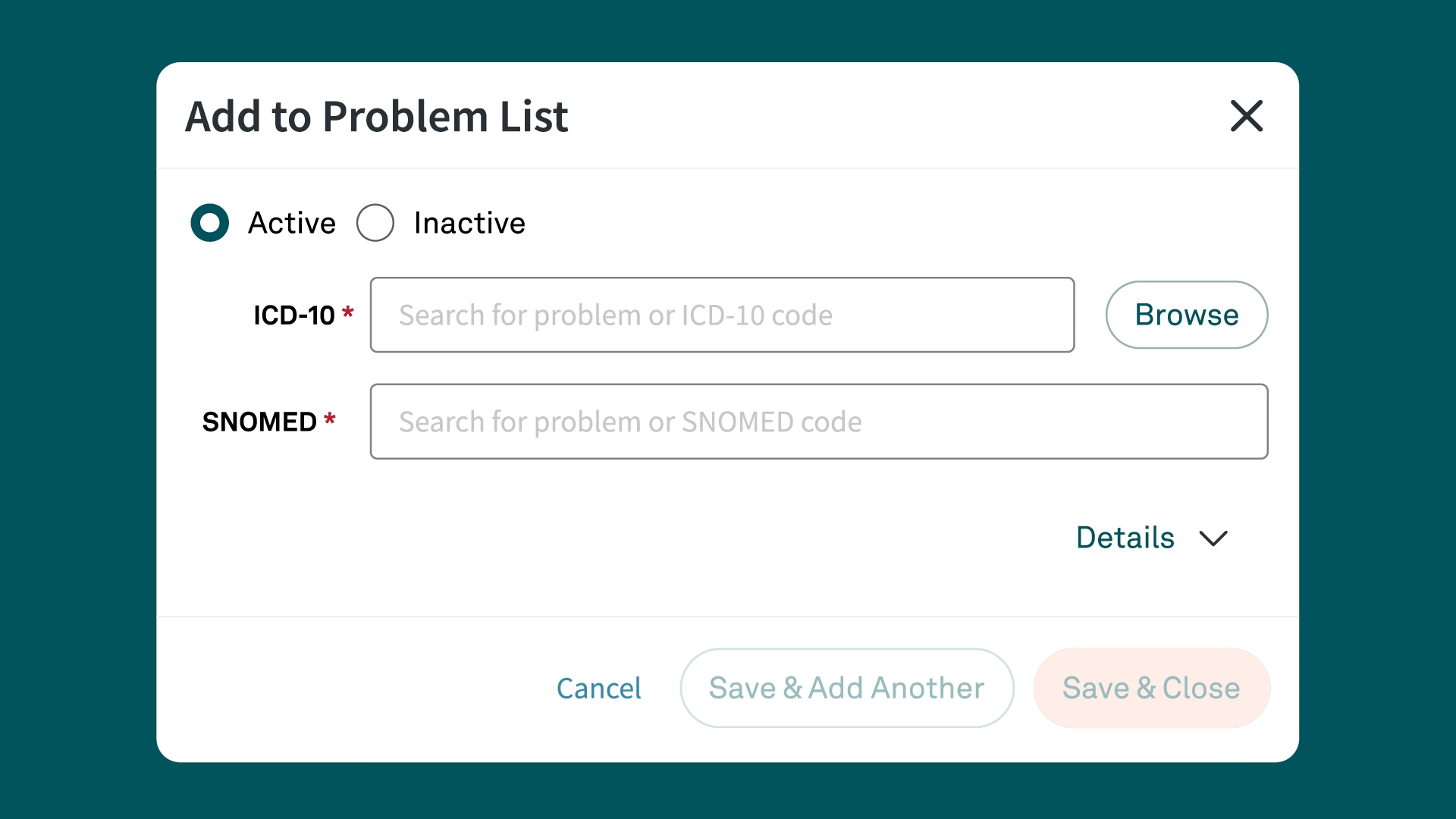
Discover how Tebra helps providers effortlessly document health-related issues and conditions in this detailed post.
Similar Codes
Subscribe to The Intake:
A weekly check-up for your independent practice



